Artificial intelligence now does the boring work for projects that used to take a whole animation team six months to finish.
Also, big companies are fighting with small artists, independent teams are getting big deals, and everyone in the business is trying to figure out what will happen next.
It’s expected that the AI animation market will reach $15.9 billion by 2030, and this rise is happening because real companies are using these tools right now.
The things that people don’t want to say about the problems that AI is causing in animation, what you need to know if you work in animation, and where this technology is going are all things that we will talk about here in this article.
What Actually Is AI in Animation?
AI in animation is basically smart software that handles the boring, repetitive stuff animators used to spend weeks doing by hand.
Here’s what it actually does. The software learns patterns from thousands of existing animations, then uses that knowledge to create new movements, backgrounds, or even entire scenes.
In fact, instead of drawing every single frame manually, you give the AI some instructions, and it fills in the gaps.
Here’s what it actually does:
- Learns patterns from existing animations and applies them to new projects
- Generates backgrounds, textures, and characters based on simple text descriptions
- Automates movements so a character’s walk looks natural without manual adjustments
- Syncs voices to lip movements automatically
- Creates variations of scenes or characters in seconds
The big difference from old-school animation is that traditional methods meant one person (or a whole team) manually creating every detail.
But AI animation means you describe what you want, and the software builds it for you. Then you refine it until it’s perfect.
It’s basically generative tools powered by deep learning algorithms that studied millions of animation samples.
We can say that it sounds fancy, but really, it just means the software got smart by watching tons of examples and now knows how things should move and look.
The Cool Stuff AI Can Do Right Now
AI art generator tools are handling tasks that used to eat up weeks of animator time.
| Animation Task | Old Way | AI Way | You Save |
| Full character rig | 50 hours | 5 hours | 45 hours |
| Lip sync (10 minutes) | 25 hours | 2 hours | 23 hours |
| Detailed background | 4 days | 3 hours | 29 hours |
| Motion capture setup | 8 hours | 1 hour | 7 hours |
| 50 unique assets | 15 days | 1 day | 14 days |
1. Motion Capture Automation
Software can now watch regular video and turn it into character animation without any special equipment.
What This Actually Does:
| Capability | What It Means |
| Body movement tracking | Records how people walk, run, and jump from normal footage |
| Facial expression capture | Catches eyebrow raises, smiles, and frowns automatically |
| Physics correction | Fixes wonky movements so everything looks natural |
| Multi-character scenes | Tracks several people at once for crowd scenes |
| Style adaptation | Applies realistic motion to cartoon or fantasy characters |
Popular tools include:
- DeepMotion (handles full body tracking)
- Reallusion iClone (for 3D modeling services)
- Rokoko Vision (affordable for small teams)
2. AI Voice Sync
Here, the software listens to dialogue and makes mouths move in perfect sync. So, we say goodbye to all those frame-by-frame adjustments to match lips with words.
Core features are:
| Feature | Benefit |
| Automatic lip matching | Syncs mouth shapes to any audio file |
| Multi-language support | The same animation works for English, Spanish, and Japanese dubbing |
| Emotion recognition | Adds smiles and frowns based on voice tone |
| Timing precision | Handles pauses and comedic beats accurately |
| Real-time preview | See results while recording voiceover |
Leading software includes:
- Adobe Character Animator (industry standard)
- MetaHuman Animator (ultra-realistic faces)
- Synthesia (good for quick projects)
3. 2D/3D Animation Tools
These platforms combine multiple AI functions to speed up everything from character setup to final rendering. What they do includes:
| Task | Traditional Method | AI Method | Time Cut |
| Character rigging | 40-60 hours manual setup | 4-6 hours with AI assistance | 90% |
| Texture creation | Days of painting and testing | Minutes with AI generation | 95% |
| Lighting setup | Hours of trial and error | Automatic, based on scene type | 85% |
| Background building | Week of detailed work | Hours with prompt-based generation | 92% |
| Render processing | Overnight for complex scenes | Minutes with neural rendering | 88% |
Top platforms are:
- Adobe Sensei (built into Creative Cloud)
- Runway ML (great for experimental stuff)
- Cascadeur (focuses on realistic movement)
4. Creative Automation
This tech generates entire environments and assets from simple descriptions. For example, you type “cyberpunk alley at night” and then get a fully detailed scene.
Generation types are:
| What Gets Created | Speed | Quality Level |
| Background environments | 5-15 minutes | Professional grade |
| Character variations | 50+ versions in an hour | Consistent style |
| Particle effects | Real-time generation | Photorealistic |
| Crowd scenes | Hundreds of unique figures | Diverse and natural |
| Asset libraries | Unlimited variations | Production ready |
Automation tools include:
- NVIDIA Canvas (landscape and environment specialist)
- Stable Diffusion (flexible for any animation style)
- Wonder Dynamics (combines multiple AI features)
5. Virtual Production
Directors see the finished look while filming happens, not months later. But AI can render backgrounds and effects in real-time during shooting.
Current users are:
- Disney (The Mandalorian sets the standard)
- Major game studios (testing levels in real-time)
- YouTube creators (high-end look on medium budgets)
How is AI Actually Changing Animation Studios?
Studios are running differently now, and honestly, the changes are pretty wild. We’re talking complete workflow overhauls that touch everything from budgets to hiring decisions.
Production Speed Just Got Ridiculous
AI in animation has slashed production timelines by around 85% for certain tasks. The time savings pop up everywhere, and they’re kind of absurd when you list them out:
- Background creation that took weeks now finishes in days
- 3D Character rigging wraps up in hours instead of dragging on for weeks
- Rendering that used to run overnight completes during your lunch break
- Revisions happen the same day without anyone panicking about deadlines
- Teams test multiple visual styles in the time it takes for one style to be used
Small Studios Are Suddenly Competitive
A three-person indie game art team can now crank out work that looks like it came from a 30-person studio.
- Those 3D animation services and tools that used to cost $50k yearly are now $500 monthly subscriptions.
- One animator with AI assistance outputs what five animators did manually before
- Professional-grade rendering happens on regular computers, not massive render farms.
- Asset libraries generate unlimited variations without anyone buying expensive stock content.
- Marketing budgets stretch way further when production costs drop 60%
Virtual Production Changed the Game
Big studios jumped on virtual production fast once they saw the cost savings. Disney’s work on The Mandalorian proved the concept worked, and now everyone’s racing to catch up.
Benefits showing up in actual production are:
- Location costs vanish when AI generates photorealistic environments on demand
- Actors perform with proper context instead of staring at blank green screens all day
- Lighting adjusts automatically based on whatever the virtual set needs
- Reshoots cost a tiny fraction of normal because the virtual set stays available forever
- Creative decisions happen right there on set, not months later when everyone’s moved on
The Democratization Effect
YouTube channel animation creators are making content that rivals studio productions, and TikTok animators are getting hired by major companies based on stuff they made alone in their bedrooms at 2 am.
Who’s benefiting from these accessible tools:
- Film students producing thesis projects that actually look professional
- Marketing agencies offering animation services without hiring massive teams
- Educational animated content creators explaining complex topics with custom animation that they make themselves
- Game developers building gorgeous cutscenes without outsourcing to expensive studios
- Non-profits are creating powerful awareness campaigns with budgets that used to be laughable
What Big Studios Are Actually Doing
Current applications at major studios are as follows:
- Disney uses AI for crowd scenes in their live-action remakes
- Pixar experiments with AI-assisted lighting in pretty much every new release
- Netflix employs AI dubbing to expand international content way faster
- DreamWorks tests AI storyboarding tools for quicker concept approval
- Sony Animation mixes traditional hand-drawn work with AI in-betweening
The Real Impact on Workflow
Day-to-day operations changed more than job titles did, and teams structure projects totally differently now because the bottlenecks have shifted to different places.
- Old workflow used to be: concept, storyboard, model, rig, animate, light, render, composite, edit
- New workflow looks like: concept, AI-generate options, refine the good ones, direct AI animation, polish everything, deliver
The revision process especially benefits from this shift. Changes that used to force you to restart entire production phases now take a few hours.
The Part Nobody Talks About: Future of AI in Animation
AI in animation sounds amazing until you start asking uncomfortable questions.
Job Security Is Freaking People Out
More than half of entertainment workers believe animators will face a serious impact from artificial intelligence within the next couple of years. What’s actually happening to jobs is:
- Animation houses that used to hire 10 junior artists now hire 2
- Entry-level positions are vanishing because AI handles grunt work
- Internship programs are getting cut, and there are fewer hands-on learning opportunities
- Young graduates are struggling to build portfolios without entry-level positions
- The gap between school and professional work keeps widening
The Creative Soul Question
AI-generated animation can look technically perfect while feeling completely empty. Hayao Miyazaki called this the “deskilling” problem, and he wasn’t wrong.
- AI mimics styles but can’t capture emotional depth
- “Good enough” animation starts replacing “exceptional” work
- Characters lack quirks that come from human observation
- Studios chase speed and cost savings over artistic quality
- Creative automation handles decisions that need human judgment
Copyright Chaos Nobody Asked For
Well, AI models train on millions of images scraped from the internet, often without asking permission or paying anyone.
What’s going wrong legally is that:
- AI companies never disclosed what they trained their models on
- Artists are finding AI-generated work that clearly copied their style
- Studios using AI to replicate looks without hiring original creators
- Freelancers are losing contracts because clients just use AI instead
- No legal framework protects artistic style as intellectual property
Disney and Universal actually sued Midjourney after AI-generated works imitating Studio Ghibli started circulating online.
The lawsuit highlights a massive problem: if an AI learned from your copyrighted work without permission, who owns what it creates?
The current answer is basically “we have no idea, lawyers are still fighting about it.” Most AI companies just said “trust us” and hoped nobody would dig too deep.
Entry-Level Jobs Vanishing
This one hits differently because it affects the future of the entire industry. The traditional path into animation is breaking down.
- Tasks that trained new animators are now automated completely
- Studios can’t justify hiring juniors when AI does their work
- Recent graduates facing impossible “need experience” requirements
- No clear path from student to professional anymore
- Senior animators worried about who would replace them eventually
The Quality Slide Nobody Wants to Admit
When production gets easier and cheaper, standards sometimes drop. Not because people want lower quality, but because “good enough” becomes commercially viable.
Marketing departments love AI because it’s fast and cheap, and creative teams worry because fast and cheap don’t always equal good.
So the future of storytelling could go two ways:
- AI frees artists to focus on creativity
- Or AI becomes a shortcut that replaces creativity entirely.
Right now, both paths look equally possible.
What Animators Need to Do Now?
The animators surviving this shift aren’t fighting AI; they’re learning to direct it.
Treating these tools as assistants rather than threats is what separates people landing jobs from people losing them.
You don’t need to become a programmer, but you do need to understand how to get AI in animation to do what you want, while you focus on the creative stuff it can’t handle.
Skills that actually matter now are:
- Learn prompt engineering: Spend a weekend with Midjourney or Stable Diffusion, practice telling generative tools exactly what you want until outputs match your vision
- Pick 3 AI tools maximum: Master Adobe Sensei, Cascadeur, or DeepMotion deeply, rather than dabbling with everything
- Focus on storytelling hard: AI generates movements, and you just need to create performances with emotional weight and character authenticity.
- Study what AI can’t do: Human observation, body language nuance, comedic timing, and emotional truth in performance.
- Start this week – Pick one small project, use one AI tool, and learn by doing instead of worrying.
Real Projects Using AI in Animation
Disney used AI for massive crowd scenes in live-action remakes, Netflix deployed AI dubbing across dozens of languages, and Pixar cut weeks off timelines with AI-assisted lighting.
| Project | Creator | What AI Did | Result |
| The Mandalorian | Disney | Virtual production, real-time backgrounds | Cut production time by 40% |
| Infinity War | Marvel | AI-assisted VFX for Thanos | Created a photorealistic character |
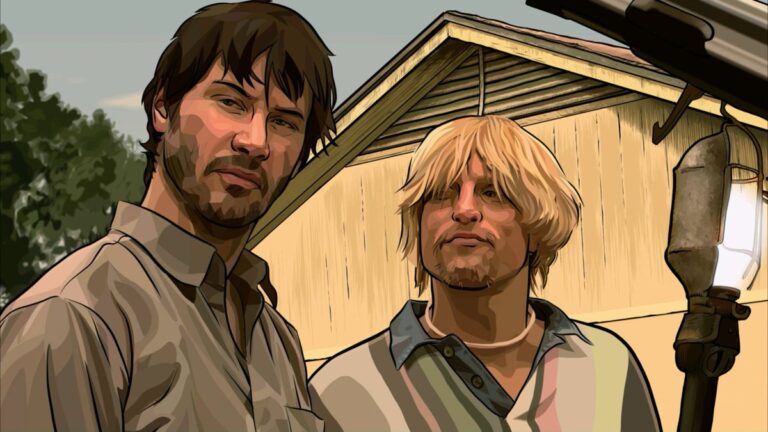
| The Irishman | Netflix | AI de-aging of actors | Reduced post-production months |
| Pocoyo episodes | Animaj | Full AI animation generation | Slashed production time by 85% |
| The Lion King remake | Disney | AI crowd and environment generation | Built massive, realistic scenes |
| Multiple Netflix shows | Netflix | AI dubbing and voice sync | Expanded to 40+ languages fast |
| Various YouTube content | Indie creators | AI backgrounds, character rigging | Professional quality, tiny budgets |
| Indie game cutscenes | Small studios | Motion capture, lip sync automation | AAA visuals without AAA costs |
Where AI Animation Is Headed Next?
The animation market is projected to hit around $587 billion by 2030, and AI is driving massive growth in ways that are already visible in studios today.
In general, neural rendering lets computers generate photorealistic images in real-time, diffusion models create professional backgrounds from simple text descriptions, and AR/VR integration with AI animation is opening up completely new interactive storytelling formats.
These aren’t distant possibilities; they’re technologies being tested and deployed right now.