Cloud gaming is significantly changing the way video games are played, both for players and gaming studio developers. This technology allows high-quality, graphically intensive titles to be streamed from remote servers instead of running on expensive, powerful local hardware.
This type of gaming not only promotes transmedia storytelling but also is more accessible on devices with minimal specifications, such as smartphones, tablets, or low-end laptops.
In this article, we will discuss how cloud gaming works, its benefits, the challenges it faces, and the applicable services.


Need Game Art Services?
Visit our Game Art Service page to see how we can help bring your ideas to life!
What Does Cloud Gaming Mean?
Cloud gaming works by shifting the heavy lifting of running a game to a powerful computer (called a server) in a distant data center. Instead of your own device doing all the complex processing and graphics rendering, the server does it for you.
Your device, whether it’s a phone, tablet, laptop, or even a low-powered PC, receives the game as a video stream, kind of like watching a YouTube video. When you press buttons, move a joystick, or click your mouse, those actions (called inputs) are sent over the internet to the server, which responds by updating the game and streaming the new visuals back to you in real time.
This setup is cost-effective because it means you don’t need to buy an expensive gaming PC or console to play high-quality games. As long as you have a decent internet connection, you can enjoy advanced game designs on almost any device, saving you the cost of pricey hardware upgrades.
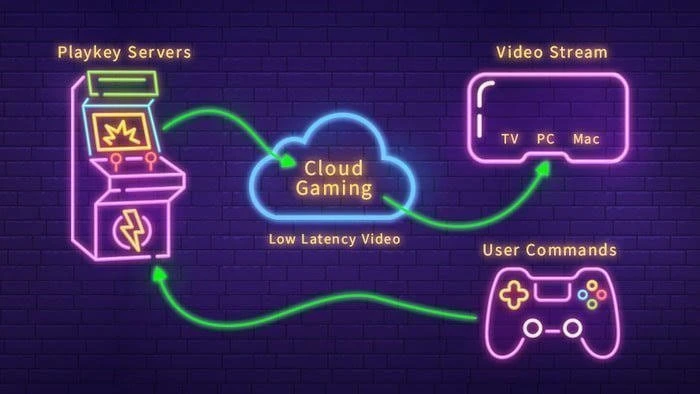
How Does Cloud Gaming Work?
At its core, cloud gaming relies on powerful servers located in data centers that run the games in real-time. The player’s actions are captured, processed immediately on the server, and the results (the video and audio of the game) are streamed back to the device in milliseconds.
A fast and reliable internet connection is vital for this process to ensure smooth gameplay even in high-graphic PC and console games. Let’s review some of the fundamental factors contributing to cloud gaming technology:
What Is the Role of Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing provides the essential infrastructure for cloud gaming. It offers scalable resources, such as server power, storage, and bandwidth, that are used efficiently.
Since these robust cloud servers handle the heavy computational tasks of the game, the load is significantly reduced on the player’s local device, resulting in a consistent gaming experience even on low-spec hardware.
Low Latency and Network Infrastructure
Low latency is a critical factor; any significant delay between a player’s input and the game’s reaction can make the experience unplayable.
To minimize this delay, providers rely on an efficient network infrastructure, which includes optimized data paths and advanced routing systems between the data center and the player. Content delivery networks (CDNs) are used by providers to specifically help reduce this lag and maintain a smooth user interface connection.
Bandwidth Requirements
To guarantee a high-quality, lag-free experience, players need sufficient bandwidth. A stable internet connection with high upload and download speeds is necessary for seamless video streaming, especially for graphics-intensive games.
For example, recommended minimum speeds for HD gameplay are 15−25 Mbps, while 4K streaming can require up to 50 Mbps. Players in areas with slower internet speeds may experience quality degradation and buffering issues.
Input Lag: The Cloud Gaming’s Main Challenge
Input lag is defined as the delay between a player’s action (for instance, pressing a button) and the game’s visible response.
Because input signals must be transmitted over the internet in cloud gaming, even small delays can negatively impact the experience, particularly in fast-paced games, intricate environment designs, or collaborative gameplay.
Reducing input lag is a primary focus, achieved by optimizing servers, improving network infrastructure, and minimizing data transfer times.
What Are the Cloud Gaming Platforms and Subscription Services?
Several companies offer cloud gaming services, with popular options including Nvidia GeForce Now, Xbox Cloud Gaming, and the now-defunct Google Stadia. Below are of the most commonly used platforms:
- NVIDIA GeForce Now: This one is a bit different; it lets you play games that you already own on some digital storefronts.
- Microsoft xCloud (Console, PC, Mobile): The cloud gaming element of Xbox Game Pass Ultimate.
- Amazon Luna: Amazon’s cloud gaming service, with Twitch integration.
- PlayStation Now: Sony’s game-streaming service that grants access to a library of PS games.
These platforms typically operate on a subscription-based model, where a monthly fee grants access to a game library or allows streaming of the user’s own supported game collection. Each service provides different levels of performance, game libraries, and device compatibility.
Device Compatibility and Accessibility for Cloud Gaming
One major benefit of cloud gaming is its compatibility with a wide variety of devices, from smart TVs to mobile phones, meaning users aren’t required to own high-end hardware.
As long as a device can run a compatible app or web browser, players can enjoy games anywhere. This accessibility also extends to supporting adaptive controllers and customizations for users with disabilities.
This includes:
- Smartphones and tablets
- Smart TVs
- Low-end laptops and desktops
- Web browsers
- Streaming Devices (e.g., Chromecast, Amazon Fire TV)
What Is the Impact of 5G Technology on Cloud Gaming?
The arrival of 5G technology is poised to revolutionize cloud gaming due to its ability to deliver faster data speeds and lower latency.
This promises improved performance, especially for mobile gaming, where previous network technologies often struggled with stability and bandwidth. The ultra-low latency of 5G is particularly effective at minimizing input lag, making real-time online gameplay much smoother.
Increased Bandwidth
5G networks offer higher bandwidth, which translates to faster download speeds and the ability to stream higher-quality games. This is critical for cloud gaming services that need to transfer large amounts of data for smooth, graphics-intensive content delivery.
Low Latency
The most significant improvement 5G brings is ultra-low latency, which reduces the delay between a player’s input and the game’s reaction. This ensures more responsive and enjoyable gaming experiences, even when playing on a mobile network.
Network Slicing
Network slicing is a 5G feature that allows providers to create dedicated virtual networks for specific applications like cloud gaming. This practice helps to prioritize gaming traffic and ensures stable performance, thereby improving the overall user experience.
Mobile Gaming
The benefits of 5G are expected to cause mobile cloud gaming to flourish, enabling various mobile game art styles, up to console-quality games, to be played on tablets and smartphones with enhanced graphics and minimal latency.
What Are the Advantages of Cloud Gaming?
Cloud gaming offers several key benefits:
- Cost Efficiency: Eliminates the necessity of purchasing expensive gaming hardware.
- Instant Access: Games can be played immediately without the wait time for downloads or updates.
- Cross-Platform Play: Players can seamlessly switch between various devices, including PC, console, and mobile.
- Game Library: Provides access to a large library of games without needing to purchase and own each title individually.
What Are the Challenges of Cloud Gaming?
Cloud gaming has the potential to be big, but is also fraught with challenges:
- Dependence on Internet Speed: The experience becomes frustrating due to poor quality and lag without a strong internet connection.
- Input Lag: While improvements are being made, input lag remains a significant drawback, particularly for competitive gamers.
- Game Library: Not every game is available on all cloud gaming platforms, which limits player choice.
What Is the Future of Cloud Gaming?
The future of cloud gaming looks very promising due to ongoing technological advancements. Further expansion of 5G networks, enhancements in server infrastructure, and continued reduction in latency will make the cloud gaming experience even more immersive and broadly accessible.
As the model gains more adoption, an increase in game libraries and innovative services is expected, potentially leading cloud gaming to become the dominant model in the gaming industry.
Final Words
Cloud gaming is revolutionizing how we experience games, opening up high-quality gaming to a broader audience. Despite some hurdles, ongoing technological improvements, like faster 5G networks and better internet infrastructure, are poised to address many of these issues.
As these advancements continue, cloud gaming has the potential to become the leading approach in the gaming world.