Visual effects (VFX) have become a cornerstone of filmmaking, television production, gaming, and beyond as the industry evolves on a daily basis.
From mind-blowing action scenes to immersive fantasy worlds, VFX artists transform the impossible into stunning visual realities. From action-packed scenes to fantastical worlds, they blend creativity and technology seamlessly.
But what exactly does a VFX artist do? And what does it take to succeed in this creative and highly technical field?
Pixune Studios’ VFX artists are the magicians of visual storytelling. They push the boundaries of what’s possible and enhance media experiences. Their work opens new avenues for storytelling and captivates audiences worldwide.
This role begins with conceptualization and previsualization, progresses through production with detailed modeling and animation, and concludes in post-production, where digital elements are merged with live footage.
In this article, we’ll explore the responsibilities, skills, processes, and career development of VFX artists, as well as the tools they use and the industry trends shaping their work.

Need Animation Services?
Visit our Animation Service page to see how we can help bring your ideas to life!
What Are The Responsiblities of a VFX Artist?

The role of a VFX artist entails a wide range of tasks, depending on the project and the specific visual effects needed.
Below, we will briefly review some of the most common tasks VFX artists manage:
1) Creating Digital Effects:
One of the primary responsibilities of a VFX artist is to generate digital effects that would be difficult or impossible to capture on camera. This includes creating explosions, weather effects, digital characters, and even entire environments using specialized software.
2) Compositing:
Compositing is a key VFX feature that involves combining visual elements from different sources, such as live-action footage and CGI, to create a single, cohesive scene. Through compositing, VFX artists ensure that all elements blend together seamlessly so the final product looks as realistic as possible.
3) 3D Animation and Motion Graphics:
Many VFX artists specialize in 3D animation and motion graphics. These professionals animate digital models and environments, often working on character rigging, particle effects, and dynamic simulations such as smoke or water.
Motion graphics are frequently used in advertising, branding, and title sequences, providing visual flair and style.
Artists also deploy 2D VFX in 3D animations to weave a vintage yet captivating tone into their pictures.
4) Enhancing Real Footage:
In many cases, VFX artists are called upon to enhance real footage by adjusting lighting, color, and texture. They might erase unwanted objects from a scene or add elements not present during filming. These subtle enhancements can make a huge difference in the overall quality of the production.
5) Collaboration with Directors and Producers:
VFX artists work closely with directors, producers, and other post-production team members to bring a vision to life. This requires strong communication skills and a willingness to adapt to creative feedback, ensuring that the VFX serves the project’s overall storytelling.
The Essential Skills of Every VFX Artist!

To excel as a VFX artist, one needs more than just technical knowledge of software tools. This role demands a unique blend of creativity, problem-solving, and collaboration.
Here are some of the must-have skills every VFX artist must develop:
1) Strong Artistic Vision:
A VFX artist must have a well-trained artistic eye to create visually stunning effects that complement the project. Understanding principles of color, lighting, perspective, and composition is critical to making effects look realistic and aesthetically pleasing.
2) Technical Proficiency in Software:
VFX artists must be proficient in a variety of industry-standard software programs. Adobe After Effects, Nuke, Houdini, Maya, and Cinema 4D are among the most commonly used tools for creating digital effects.
3) Problem-Solving Skills:
Unexpected challenges are part of the job in VFX. Whether blending CGI with live-action footage or troubleshooting a rendering issue, VFX artists must be knowledgeable and adaptable enough to constantly find creative solutions to technical issues.
4) Attention to Details:
Even the tiniest oversight in a visual effect can disrupt the audience’s immersion.
VFX artists must have a meticulous eye for detail to ensure that every effect—no matter how minor—blends seamlessly into the rest of the footage.
5) Time and Resource Management:
Given the time-sensitive nature of many productions and the costs of 3D VFX, artists often work under tight deadlines. Effective time and resource management is essential to ensure that tasks are completed on schedule without compromising quality.
6) Teamwork Attitude:
Collaboration is a significant part of the VFX industry. Artists must be able to communicate clearly with other team members, including animators, editors, and sound designers, to achieve the desired outcome.
Being open to feedback and constructive revisions is also a vital aspect of the job.
The VFX Process: How Are Visual Effects Created?
The process of creating visual effects for a project is highly structured and involves several steps.
From pre-production planning to final delivery, VFX work is both an art and a technical science.
Pre-Production and Planning!
Before any visual effects work begins, the VFX team is brought into the pre-production phase of the project. They collaborate closely with the director and production team to determine the scope of the visual effects, decide which scenes will require CGI, and create initial concepts for the effects.
Storyboards and concept art are crucial in determining the final product’s outlook.
Asset Creation!
Once planning the initial idea is complete, the VFX team begins creating the required assets.
This step may entail 3D models, textures, environments, and characters, as well as multiple artists working together to create and animate such materials.
Animation and Simulation:
This step involves bringing 3D models to life through movement, whether animating a character or simulating the movement of particles like smoke or fire.
With VFX in the 3D animation pipeline, artists also use motion tracking to align CGI elements with live-action footage.
Compositing:
In this stage, VFX artists blend all the visual elements into the live-action footage, making adjustments to ensure that everything fits together seamlessly.
This step involves color correction, rotoscoping (eliminating unwanted elements), and layering the various components.
Final Rendering!
Rendering is the process of exporting the final product from the software.
Despite the simple definition, 3D rendering can be one of the most time-consuming parts of the process, as complex effects require significant computational power.
The visual effects are reviewed once the rendering is complete and possible final adjustments are made.
Different Types of Visual Effects
Visual effects can be broadly categorized into two main types: practical effects and digital effects.
In the following, we have more closely examined 4 common yet different types of VFX:
Practical Effects:
Practical effects are physical, real-world effects captured on camera, Including explosions, miniature models, and animatronics.
While practical effects have become less common since the advances of digital VFX, they are still combined with digital effects to enhance realism.
Digital Effects:
Digital effects, or the so-called CGI, are created entirely through software.
This modern VFX technique includes various fields such as 3D modeling, animation, compositing, and digital matte painting.
Digital effects are incredibly versatile and are equipped to create everything from subtle enhancements to fully immersive digital environments.
3D Effects:
3D effects are used to create lifelike models and environments that can be animated and integrated into live-action footage.
This method includes character animation, vehicle simulations, and dynamic effects such as water, fire, or explosions.
2D Effects:
2D effects, such as motion graphics and compositing, involve working with flat images or footage. These effects are often used for interface animations, title sequences, and simple enhancements like adding smoke to a scene.
What Are The Industry Applications of VFX?
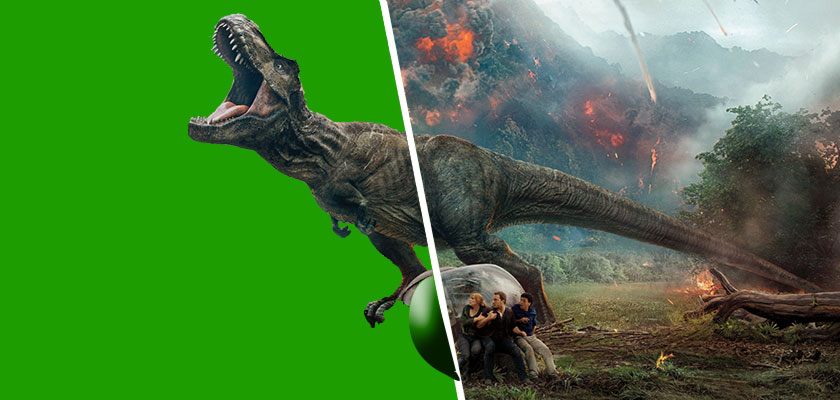

VFX artists’ work is not solely limited to the film and television industry. Visual effects are applicable across various visual-oriented fields, each requiring a unique approach to the visual impacts.
The Film and Television Sector
The most well-known application of VFX is in film and television production.
VFX artists create everything from stunning action sequences to mythical creatures, transforming how stories are told on screen.
Blockbuster films often rely heavily on visual effects to create stunning and popular worlds and characters that would otherwise be impossible to portray.
Video Games Development
VFX artists work closely with game designers and developers to create VFX and particle systems, and immersive experiences for players.
Their collaborations include everything from simulating realistic weather effects to creating the movements and interactions of in-game characters and environments.
Advertising and Marketing Agencies
Advertising firms frequently hire VFX artists and animators to create compelling commercials and digital content.
Motion graphics, 3D animations, and compositing are excellent approaches to highlighting products, creating captivating brand narratives, and engaging audiences with dynamic visuals.
Virtual and Augmented Reality
With the recent advances in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), VFX artists are increasingly involved in creating immersive digital environments for such purposes.
In these applications, VFX artists must ensure that the visual effects are not only realistic and interactive but also responsive to user inputs in real-time.
Architecture and Traditional Design
VFX artists also contribute to architecture and design projects by creating photorealistic 3D renderings of buildings and spaces.
VFX have long allowed architects and designers to visualize their concepts and present their initial work to clients before construction begins.
Every Artist's Toolbox: The Best VFX Software and Tools
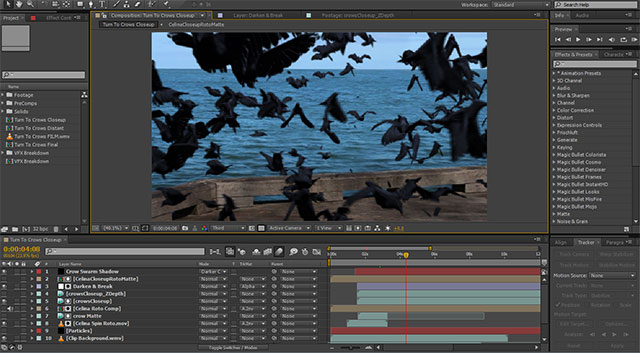
VFX artists rely on many tools to create their visual effects.
The following are some of the most commonly used programs in this evolving field:
Adobe After Effects
Widely used for compositing, motion graphics, and visual effects, After Effects is a versatile tool that allows artists to create everything from simple motion graphics to complex layered compositions.
Nuke
Offering a node-based interface, Nuke is powerful compositing software favored by many professionals in the VFX industry.
Nuke’s platform provides total control and flexibility when working with complex visual effects.
Houdini
Houdini is a 3D animation and visual effects software with advanced simulation capabilities.
This software is often used to create dynamic effects such as smoke, fire, and water, particle systems, and procedural models such as buildings and environments.
Houdini’s interface and features allow artists to create customizable and reusable effects, making it a go-to tool for complex VFX work.
Autodesk Maya
Maya is one of the leading 3D animation software tools used in the industry for modeling, rigging, animating, and rendering 3D assets.
VFX artists use Maya to create everything from animated characters to realistic environments. Maya’s versatile options make it a popular choice for many 3D visual effects artists.
Blender
Blender is an open-source 3D creation suite that has become a significant player in the VFX industry due to its wide range of features and active community support.
This platform offers modeling, texturing, animation, and compositing tools and is an excellent choice for freelancers and studios looking for a cost-effective solution.
You can use our comparative study on Maya vs. Blender to choose which platform best meets your production needs.
The VFX Artist Career Path Landscape

The career path of a VFX artist can vary greatly depending on their skills, interests, and the industry they choose to work in.
While some VFX artists may focus on specific aspects of visual effects, such as animation or compositing, others may pursue broader roles in supervision or production.
In the following, we have briefly reviewed some of the most common positions of VFX artists in various industries:
Entry-Level Roles:
Most VFX artists begin their careers in entry-level positions such as junior compositor, 3D modeler, or motion graphics artist.
These primary roles provide hands-on experience and allow artists to build their portfolios while learning the ins and outs of their favorite fields.
Mid-Level Positions:
After some fundamental experiences, VFX artists can move into more specialized roles, such as lead compositor, effects animator, or lighting artist.
At this stage, artists typically take on more responsibilities and may lead small teams and oversee specific tasks within a project.
Senior and Supervisory Roles:
More experienced VFX artists now have the opportunity to move on to senior roles such as VFX supervisor or creative director.
These positions involve managing larger teams, collaborating closely with producers, and ensuring the visual effects align with the project’s overall vision.
Freelancing and Studio Work:
Many VFX artists choose to work as freelancers, offering their services to multiple clients and studios.
While freelancing provides flexibility and variety, it also requires strong self-promotion and business skills.
Alternatively, VFX artists can also work full-time at VFX studios, production houses, or post-production companies, where they can have stable employment and opportunities for long-term growth.
Learning and Development:
The VFX industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques emerging all the time.
VFX artists must continually update their skills and knowledge to stay ahead in the competition.
This can involve learning new software tools, attending industry workshops, or taking online courses in areas like virtual production, AI-driven animation, or real-time rendering.
2024 Trends in VFX: What to Do Next?
The world of visual effects is ever-changing. From evolving technological advances to shifting audience expectations and the growing demand for more immersive visual experiences, VFX remains a multidimensional visual art.
Several key trends, however, are currently shaping the future of the VFX industry:
Real-Time Rendering and Virtual Production:
Real-time rendering technologies, such as those used in game engines like Unreal Engine and Unity, are revolutionizing the VFX industry.
These tools allow the creation of visual effects in real-time and dramatically reduce the time it takes to produce high-quality scenes.
Virtual production, which combines real-time rendering with physical sets and actors, is becoming increasingly popular in film and television, such as projects like The Mandalorian.
AI and Machine Learning in VFX:
As with most industries, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are beginning to make their mark in VFX as well.
These technologies can automate certain routine tasks, such as rotoscoping and motion tracking, which traditionally require significant manual effort.
AI-driven tools can also generate more realistic textures, lighting, and animations, opening up new possibilities for visual effects.
Immersive Experiences: VR and AR
As virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) continue to grow, VFX artists are increasingly involved in creating immersive digital experiences.
- In VR, artists must create fully 3D environments that allow users to explore and interact with their surroundings.
- In AR, VFX artists must ensure that digital elements blend seamlessly with the real world to enhance the user experience without disrupting immersion.
Advances in Motion Capture:
Motion capture technology (recording an actor’s actual movements and translating them into digital character animations) has become more sophisticated in recent years.
New systems allow greater precision and realism for capturing body movements, facial expressions, and subtle gestures.
These new findings have opened up new possibilities for character animation in film, video games, and even virtual humans in interactive media.
Higher Demand for Streaming Content:
The rise of streaming platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ has led to an explosion in demand for high-quality visual effects in television shows and films.
With more content being produced than ever before, VFX artists are in high demand to create compelling visuals that can compete in the crowded entertainment landscape.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly VFX:
As awareness of environmental issues grows, the VFX industry is also exploring ways to reduce its carbon footprint.
Many studios are now adopting more energy-efficient rendering processes and reducing the physical waste generated by production.
Virtual production, which minimizes the need for travel and physical sets, is one example of how VFX is becoming more sustainable.
Final Words
The role of a VFX artist is both highly creative and technically demanding, requiring a deep understanding of visual storytelling, software tools, and industry workflows.
VFX artists are the heart of bringing imaginative worlds and characters to life, from film and television to video games and virtual reality.
With technology’s constant growth and the increasing demand for immersive visual experiences, the VFX industry offers exciting opportunities for those with a passion for both art and technology.
As the boundaries between the real and digital worlds continue to cross, the work of VFX artists will only become more integral to how we experience media.
Whether you’re aspiring to become a VFX artist or simply curious about the process behind your favorite films and games, understanding the skills, tools, and trends that are shaping this dynamic field can provide valuable insights into the future of visual effects.








