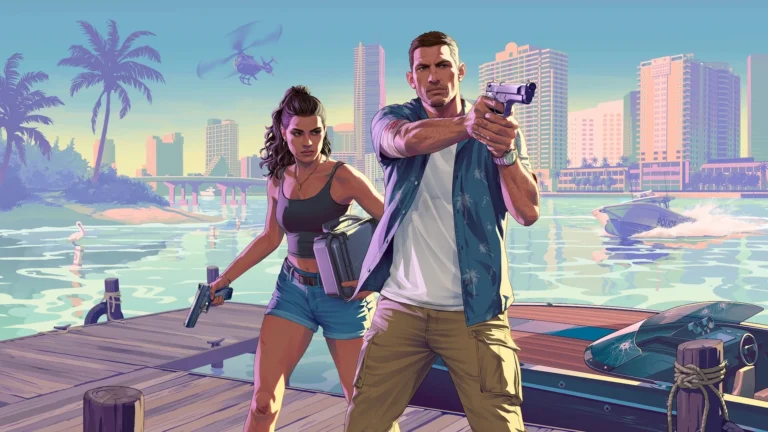
The realistic art style is a form of art that aims to depict subjects as they appear in real life, with a high level of detail and accuracy. Video games have evolved significantly over the years, not only in terms of gameplay and storytelling but also in visual aesthetics. One of the most notable shifts has been the embrace of realistic art styles, where game developers strive to create immersive, lifelike environments and characters.
In this article, we delve into the technical aspects of realistic art style in games, exploring its historical roots, production pipeline intricacies, and the impact it has on the gaming industry.


Need Game Art Services?
Visit our Game Art Service page to see how we can help bring your ideas to life!
I- Historical Context
I-I- Early Years: Origins of Realistic Art in Games
The journey toward realistic game graphics traces back to the early days of gaming when pixelated sprites dominated the screen. As technology advanced, developers sought ways to break free from the constraints of pixel art, paving the way for the birth of 3D graphics. The transition from 2D to 3D game art styles marked a paradigm shift, opening up new possibilities for creating more visually engaging and immersive gaming experiences.
I-II- Advancements in Graphics Technology
The late 20th century witnessed rapid advancements in graphics technology, with the introduction of dedicated graphics processing units (GPUs) and more sophisticated rendering techniques. This allowed developers to experiment with lighting, shading, and texture mapping, bringing a level of realism previously unseen in the gaming world.
I-III- Shift from Pixel Art to 3D Realism
The introduction of 3D realism revolutionized game design, offering developers the ability to craft expansive worlds and intricate characters. Early attempts at realism often faced technical limitations, but the pursuit of more convincing graphics persisted. Games like “Myst” (1993) and “Final Fantasy VII” (1997) played pivotal roles in pushing the boundaries of what was visually achievable in gaming.
I-IV- Rise of Realism in the 21st Century
The 21st century witnessed an exponential leap in graphical fidelity. With the advent of powerful gaming consoles and high-performance PCs, developers could incorporate advanced rendering techniques, high-resolution textures, and realistic physics simulations. Games like “Crysis” (2007) became synonymous with pushing hardware to its limits, showcasing the industry’s commitment to achieving unparalleled realism.
In the following sections, we will explore the technical intricacies of using realistic art styles in, game art outsourcing from the graphics engines and rendering techniques to the production pipeline that brings these virtual worlds to life.

II- Technical Aspects of Realistic Art Style
II-I- Graphics Engines and Rendering Techniques
Overview of Rendering Pipelines: Realistic game graphics are made possible through sophisticated rendering pipelines that simulate the behavior of light and its interaction with virtual objects. Modern graphics engines, such as Unreal Engine and Unity, employ complex rendering techniques like Physically Based Rendering (PBR) to achieve lifelike materials and lighting. The rendering pipeline involves stages such as geometry processing, rasterization, shading, and post-processing effects.
Shader Development for Realistic Lighting and Shadows: Shaders play a crucial role in defining how light interacts with surfaces in a game. Realistic lighting models, including global illumination and ambient occlusion, contribute to creating convincing environments. Advanced shadow mapping techniques, like cascaded shadow maps or Percentage Closer Soft Shadows (PCSS), enhance the quality of shadows, adding depth and realism to scenes.
II-II- High-Resolution Textures and Asset Creation
Role of Texture Mapping: The use of high-resolution textures is a cornerstone of realistic art in games. Texture mapping involves applying detailed textures to 3D models to simulate surface details like roughness, reflections, and imperfections. This meticulous process requires artists to create textures at resolutions that capture intricate details, from the grain of wood to the fine pores on a character’s skin.
Challenges and Innovations in Asset Design: The creation of realistic game asset designs, whether characters or environments, poses challenges in terms of data size and performance. Developers often employ techniques like texture atlases and MIP mapping to optimize memory usage while maintaining visual fidelity. Additionally, innovations in asset design include the use of procedural generation to dynamically generate textures and details, reducing the manual workload on artists.
II-III- Animation and Rigging
Realistic Character Animation: Achieving realistic character animation involves intricate rigging and animation techniques. Rigging, the process of creating a skeleton and control systems for a character, allows for natural movement and expressions. Motion capture technology has become integral to realistic animation, enabling developers to record and transfer real-world movements onto virtual characters, resulting in lifelike actions and facial expressions.
Rigging Techniques for Lifelike Movement: Rigging for realism requires careful attention to joint movements, muscle deformations, and facial rigging. Advanced rigging systems simulate the physics of muscles and joints, providing a more accurate representation of how a character moves. Rigging artists collaborate with animators to ensure that the character’s movements align with the laws of physics, enhancing immersion for players.
II-IV- Sound Design and Realism
Importance of Immersive Audio: Realism in games extends beyond visuals to include audio. Immersive sound design contributes significantly to the overall realistic experience. Spatial audio, dynamic soundscapes, and realistic environmental sounds enhance the player’s sense of presence within the game world. The integration of 3D audio technologies further elevates the immersive qualities of realistic game environments.
Integration with Visual Realism: To achieve a seamless blend of visual and auditory realism, developers integrate sound design with the visual elements of the game. For example, the sound of footsteps may vary depending on the surface a character is walking on, creating a cohesive and immersive experience. This integration enhances the player’s ability to suspend disbelief and become fully engrossed in the virtual world.
In the upcoming sections, we will unravel the intricate production pipeline of realistic game development, exploring the stages from conceptualization to testing, and highlighting the challenges and solutions along the way.

III- Production Pipeline
III-I- Conceptualization and Pre-Production
The journey towards a realistic game begins with a solid conceptual foundation. Concept artists play a pivotal role in visualizing the game’s characters, environments, and overall aesthetics. The emphasis on realism requires artists to pay attention to detail, considering not only the visual aspects but also the mood and atmosphere they want to convey. High-quality concept art serves as a roadmap for the entire development team, guiding them through the creation of a cohesive and immersive world.
Realistic environments demand meticulous planning. Level designers and environmental artists collaborate to ensure that the virtual world feels authentic and coherent. Considerations include the scale of objects, the placement of assets, and the overall architecture. Planning involves a balance between realism and gameplay, ensuring that the environment not only looks convincing but also serves the needs of the game’s mechanics.
III-II- Modeling and Texturing
High-Poly vs. Low-Poly Models: The creation of 3D models is a critical step in the production pipeline. Artists often start with high-poly models, capturing intricate details and nuances. However, the use of high-poly models can be resource-intensive. To address this, developers employ techniques like normal mapping to transfer the details of high-poly models to low-poly counterparts efficiently. This allows for realistic visual fidelity without sacrificing performance.
UV Mapping for Realistic Textures: UV mapping is a crucial aspect of texturing, ensuring that textures are applied to 3D models accurately. In realistic game development, UV mapping becomes even more intricate due to the need for high-resolution textures. Artists must carefully unwrap the model to optimize the use of texture space, ensuring that details are accurately represented without distorti
III-III- Rigging and Animation
Rigging Realistic Characters: Rigging realistic characters involves creating a skeleton that mimics human or creature anatomy. Rigging artists use sophisticated tools to define joints, control mechanisms, and skin deformation. The goal is to enable animators to achieve natural and lifelike movements. Rigging for realism often includes features such as inverse kinematics and muscle simulations, adding a layer of authenticity to character animation.
Motion Capture and Realism in Animation: Motion capture has become a cornerstone of realistic character animation. Actors perform movements in a controlled environment, and the captured data is then applied to virtual characters. This technology allows for nuanced movements, facial expressions, and even subtleties like weight shifts during walking. Motion capture brings an unparalleled level of realism to character animation, contributing to the overall immersive experience for players.
III-IV- Integration and Testing
Challenges in Combining Realistic Elements: As various elements of the game come together, developers face the challenge of seamlessly integrating realistic assets, animations, and environments. Ensuring that lighting is consistent, textures align correctly, and animations play smoothly requires meticulous attention to detail. Realistic games often go through extensive testing and optimization to achieve a balance between visual fidelity and performance.
Testing for Realism and Player Experience: User experience testing is crucial to evaluating the success of realistic game design. Testing goes beyond technical aspects to assess how players perceive and interact with the realistic elements. Feedback from players helps developers refine the gaming experience, addressing any issues that may disrupt immersion or hinder gameplay.
In the following sections, we explore the benefits of realistic art styles, including their impact on player engagement, marketing, and the broader gaming industry. Additionally, we delve into the challenges faced by developers and the innovative solutions that drive the evolution of realistic game design.

IV- Benefits of Realistic Art Style
The primary advantage of a realistic art style is its ability to immerse players in a visually captivating virtual world. Realistic environments, characters, and animations contribute to a heightened sense of presence, allowing players to feel more connected to the game universe. This immersion enhances the overall gameplay experience, drawing players into a narrative or gameplay scenario with greater emotional impact.
Realistic graphics often serve as a powerful marketing tool. High-quality visuals showcased in trailers, screenshots, and promotional materials grab the attention of potential players. The allure of realistic art styles can contribute to increased interest and anticipation for a game. As a result, games with impressive realism tend to generate more pre-release buzz and, consequently, higher sales upon launch.
The visual quality of a game significantly influences how it is received by critics and players alike. Realistic art styles often receive praise for their attention to detail, graphical fidelity, and the level of craftsmanship involved. Positive reviews and high ratings can, in turn, attract a larger audience, as players are more likely to explore titles that receive acclaim for their visual excellence.
In the realm of virtual reality, realistic graphics play a pivotal role in creating convincing and immersive VR experiences. The depth and fidelity of realistic art styles contribute to a sense of presence, minimizing the gap between the virtual and real worlds. VR games that prioritize realism can deliver unparalleled levels of immersion, making players feel as if they’ve stepped into another reality.
V- Challenges and Solutions
V-I- Hardware Limitations
The pursuit of realism often faces challenges related to hardware limitations. Achieving high levels of graphical fidelity may require powerful GPUs and CPUs, potentially excluding players with less robust gaming setups. Developers must find a balance between pushing visual boundaries and ensuring accessibility across a range of gaming platforms.
V-II Performance Optimization
Realistic games can be demanding on system resources. To address this, developers implement performance optimization techniques, including level-of-detail (LOD) systems, efficient texture compression, and dynamic rendering adjustments. These optimizations aim to provide a smooth gaming experience without sacrificing visual qualit
V-III- AI-driven Graphics Enhancements
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays an increasingly significant role in enhancing realistic graphics. AI algorithms can be used to upscale textures, generate realistic facial expressions, and even simulate complex natural phenomena like weather and vegetation. These innovations allow developers to achieve higher levels of realism without solely relying on raw computing power.
V-IV- Cross-Platform Realism
Developers are exploring ways to bring realistic graphics to a broader audience by optimizing games for various platforms. Cross-platform development, coupled with scalable graphics settings, ensures that players on both high-end PCs and less powerful consoles can enjoy a visually compelling experience. This approach expands the reach of realistic games, making them accessible to a diverse gaming community.
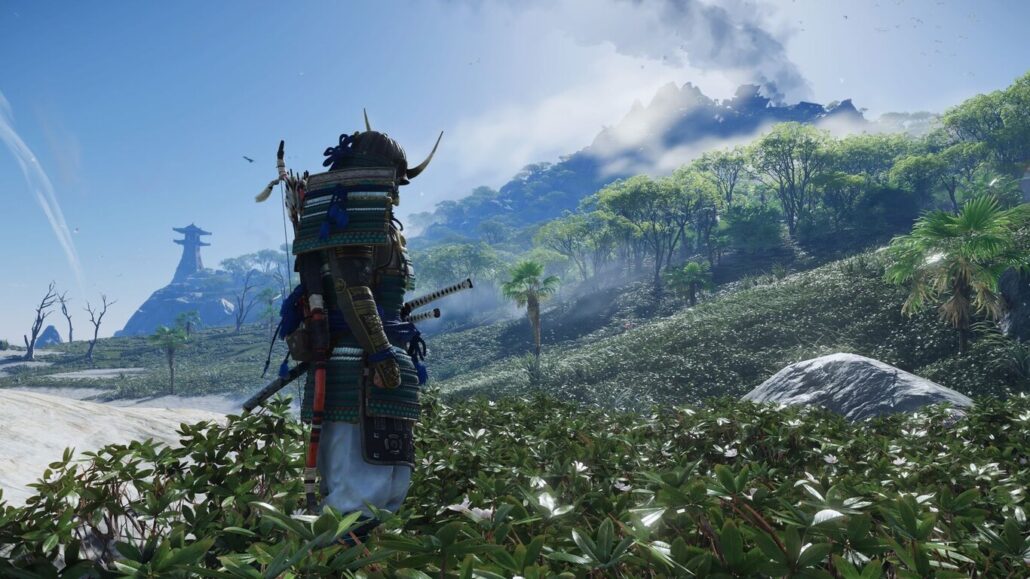

VI- Case Studies
VI-I- "Red Dead Redemption 2" (2018)
Rockstar Games’ “Red Dead Redemption 2” stands as a testament to the power of realistic art in gaming. The game’s vast open-world, meticulously crafted environments, and attention to detail in character animations set new standards for realism. The use of advanced rendering techniques, including a dynamic lighting system and realistic weather effects, creates a visually stunning and immersive Wild West experience for players
VI-II- "The Last of Us Part II" (2020)
Naughty Dog’s “The Last of Us Part II” is a narrative-driven masterpiece that seamlessly integrates realistic graphics with emotional storytelling. The game’s highly detailed environments, lifelike character models, and fluid animations contribute to the emotional impact of its narrative. Realistic lighting and shadow effects enhance the atmosphere, creating an immersive experience that resonates with players.
Games with realistic art styles often foster dedicated and engaged communities. Players appreciate the effort put into creating visually stunning worlds, and the realism enhances social and online interactions. Screenshots and videos shared within gaming communities showcase the beauty of the virtual worlds, sparking discussions about the technical achievements and artistic merits of these games.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey of realistic art in games has been marked by technological advancements, creative innovation, and a commitment to pushing the boundaries of what’s visually achievable. From the early days of pixelated sprites to the photorealistic landscapes of today, game developers continue to explore the possibilities of realistic graphics.
As technology evolves, challenges in hardware limitations and performance optimization are met with ingenious solutions, including AI-driven enhancements and cross-platform development. Successful games like “Red Dead Redemption 2” and “The Last of Us Part II” showcase the impact of realistic art styles on player engagement, marketing, and the gaming industry as a whole.
Looking ahead, the future of realistic game design holds exciting prospects. Emerging technologies, such as ray tracing and advancements in AI, promise to further elevate the level of realism in virtual worlds. As the gaming industry continues to evolve, realistic art styles will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the immersive experiences of tomorrow’s games.