Designing an engaging game interface goes beyond aesthetics. It’s about creating a seamless and enjoyable experience for players. A clear UI/UX design pipeline ensures that every interaction, from menu navigation to gameplay, feels intuitive and enhances the overall experience.
In this article, we’ll break down the stages of the UI/UX design pipeline for game interfaces. We’ll cover the key steps for creating user-friendly designs, along with essential tools and best practices every UI/UX artist and game art studio should consider.
- What Is UI/UX Design?
- Why Is UI/UX Important in Game Design?
- Stages of the UI/UX Design Pipeline
- Tools and Software for UI/UX Design
- Best Practices for Effective UI/UX Design in Games
- Case Studies


Need Game Art Services?
Visit our Game Art Service page to see how we can help bring your ideas to life!
What Is UI/UX Design?
So, you know already, UI/UX design is all about making users experience the product in a better way and get what they want. It’s not that different from game development. UI/UX design for games is focused on improving the interaction between the game (product) and player (user) interface.
There are some differences between UI and UX design. UI design addresses the visual aspect, i.e., layout, menus, and buttons, while UX design is about ensuring that the experience is seamless and intuitive. The UI/UX design process is the blueprint that describes how designers work and ensures the finished product is interactive and usable.
UX Design
UX design ensures games are intuitive, engaging, and easy to navigate. It focuses on structure and usability rather than visuals. Key steps include:
- User Research: Understanding player needs and behaviors. A process involved in game design psychology
- Wireframing and Prototyping: Structuring interfaces and testing navigation, in which game HUD design has an important role.
- Usability Testing & Iteration: Refining the experience based on feedback. Effective optimization techniques ensure your changes don’t impact performance.
- Engagement: A strong UX design keeps players engaged and reduces frustration.
Read more about The Ultimate Guide to UI/UX Design in Hypercasual Games in our dedicated blog.
UI Design
UI design focuses on the visual and interactive elements players engage with, such as menus, buttons, and HUD principles. It includes:
- Layout & Visual Design: Creating intuitive, appealing interfaces.
- Typography & Colors: Enhancing readability and directing focus.
- Interactive Elements: Designing buttons, icons, and animations for mobile games’ UI design and other types of games.
A well-designed UI enhances player involvement and usability.
Why Is UI/UX Important in Game Design?
With a well-designed UI and UX, players can enjoy a smoother and more engaging gaming experience. They can:
- Learn and navigate the game easily. Clear menus, intuitive controls, and helpful guides make it easier to get started.
- Play without frustration. A good UX ensures a seamless flow, making interactions feel natural and responsive.
- Stay connected to the game world. A clean and visually appealing UI — built on a stylized art style — helps players focus on gameplay rather than struggling with the interface.
- Make better decisions. Well-placed game elements, like health bars and mission indicators, provide crucial information at a glance.
- Avoid confusion and fatigue. A well-organized design reduces cognitive load. It allows players to enjoy the game without unnecessary distractions.
In a fast-paced action game, if the controls are clunky or important information isn’t clearly displayed, players might struggle and lose. But with a well-designed UI/UX they can stay in control and fully enjoy the experience.
Stages of the UI/UX Design Pipeline
Every designer needs to follow a structured process to create an engaging experience for game players. You should know that this process isn’t linear. UX design requires constant iterations and going back to previous steps when needed. The following stages outline the main actions needed to craft game interfaces.
Research and User Analysis
This stage is the foundation of any UI/UX design process. Every good design starts with understanding the users. In this stage, designers conduct research to understand the target audience, gather insights on user behavior, explore game genres, and analyze competitor games. User analysis helps shape decisions about what players need and expect. Findings from this stage inform design choices later in the process.
You might ask how designers go through this stage. They start by identifying the player demographics (age, experience, and preferences). It’s important to know who you are designing for. Designers should also know the platform of the game (mobile, PC, console) and how it affects player interaction.
Knowing your competitors in the market is also needed because it helps you to identify what works well in their UI and UX. You can spot weaknesses or user complaints to avoid repeating mistakes, too. For this stage, designers use various techniques to gather insights, such as surveys and user Interviews.
Wireframing and Prototyping
Wireframing and prototyping play a crucial role in game UI/UX design. They help designers plan, test, and refine interfaces before full implementation. These steps ensure that the user experience is intuitive, visually appealing, and functional without wasting development resources.
A wireframe is a basic, low-fidelity layout that outlines the structure and flow of a game’s UI. It focuses on functionality rather than aesthetics. Therefore, designers can make changes quickly.
A prototype is a clickable, interactive version of the game UI that simulates how users will navigate and interact with it. It can be low-fidelity (simple interactions) or high-fidelity (fully designed UI elements).
Iteration and Refinement
As it was mentioned, design isn’t a linear process. No design is perfect on the first try. Designers need to revisit some of the early steps to refine the design using new insight gathered from tests and user feedback.
Designers will make improvements based on playtesting, ensuring that the interface meets both functional and aesthetic needs before moving on to implementation. How do designers do it? Essentially, they test the UI with players through playtesting, usability tests, and feedback surveys to identify issues. By identifying patterns and pain points, new insights can be used for adjustments. As a designer, you need to run more tests and repeat this process until the product is intuitive and engaging.
Final Implementation
The final implementation stage is where UI/UX designers hand over their work to developers and ensure the design is correctly blended into the game. This step is crucial because even a well-designed interface can fail if not properly implemented.
First, designers provide all necessary assets, including interface layouts, visual design elements, animations, and interaction guidelines. Next, designers collaborate with developers to bring the UI design to life in game engines. Some adjustments may be needed to ensure smooth user interaction.
Finally, designers test the implemented UI to catch any inconsistencies, usability issues, or
performance problems. Any necessary refinements are made before the game’s launch to ensure a high-quality user experience.
Post-Launch Evaluation and Updates
Once the game is launched, the work isn’t over. Real player feedback helps refine and improve the UI/UX. This stage focuses on analyzing user behavior, identifying issues, and making updates to enhance the experience. First, designers and researchers collect feedback through player reviews, surveys, and usability reports. This helps uncover usability problems that weren’t visible during the development phase.
Next, based on findings, updates are made to fix issues, improve navigation, or adjust interactions for a smoother experience. Finally, this process is ongoing, and game UI/UX design evolves based on new features, player expectations, and technological advancements. Regular updates keep the interface fresh.
Tools and Software for UI/UX Design
Below are 4 of the most popular UI/UX software and tools today, with widespread adoption among game development, web design, and mobile app interface experts:
1. Figma
Figma is a real-time collaboration UI/UX design tool that works in any browser. It’s simple, fast, and excellent for interface design, prototyping, and feedback – all in one place. Ideal for distributed teams.
2. Adobe XD
Adobe XD provides high wireframing, prototyping, and high-fidelity interface design. As Adobe XD is used alongside other Adobe Creative Cloud tools, it would be a good option for designers already using software such as Photoshop or Illustrator.
3. Sketch
Sketch is a macOS darling, and its ease of use, combined with powerful vector editing capabilities, has made it a crowd-pleaser. It’s perfect for UI design and has a mature ecosystem of plugins and integrations to aid design systems and collaboration.
4. Axure RP
Axure RP is capable of easily creating high-level wireframes and interactive prototypes. It is particularly useful for UX designers who need to present user flows, conditional logic, and annoying behaviors.
Best Practices for Effective UI/UX Design in Games
To create the best possible experience for users, designers must follow these key practices:
- Prioritize simplicity and clarity to avoid overwhelming players.
- Keep consistency in design elements like buttons and icons to build familiarity.
- Focus on accessibility to ensure the game is enjoyable for all players; understanding colour theory can help choose accessible palettes.
- Iterate and test frequently because user feedback is critical to improving the design.
Case Studies
Exploring real-world examples helps understand how successful UI/UX design is applied in games. Here, we’ll briefly explore two games known for their exceptional design and address some key lessons we can learn from them.
The Last of Us – Simple and Clean Design
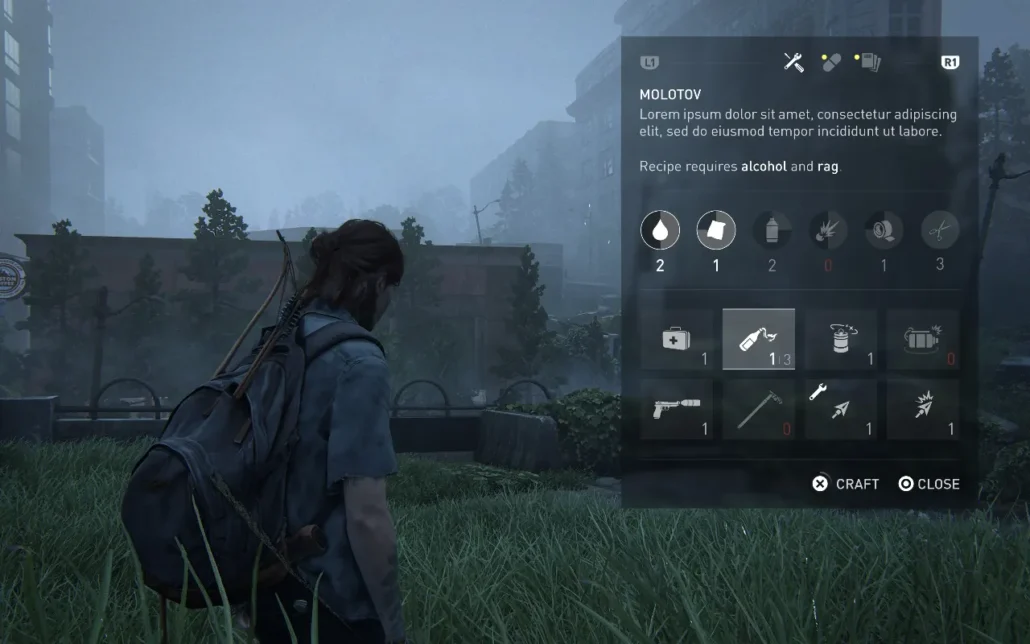
The Last of Us is known for its simple UI design. It uses very few on-screen elements, which helps players stay focused on the game and story. Things like health and ammunition are easy to see, but don’t get in the way of the player. Keeping the interface simple and subtle prevents distracting the player from the game.
Note: Keep the UI clean and don’t clutter the screen with too many details.
Fortnite – Easy Navigation and Accessibility
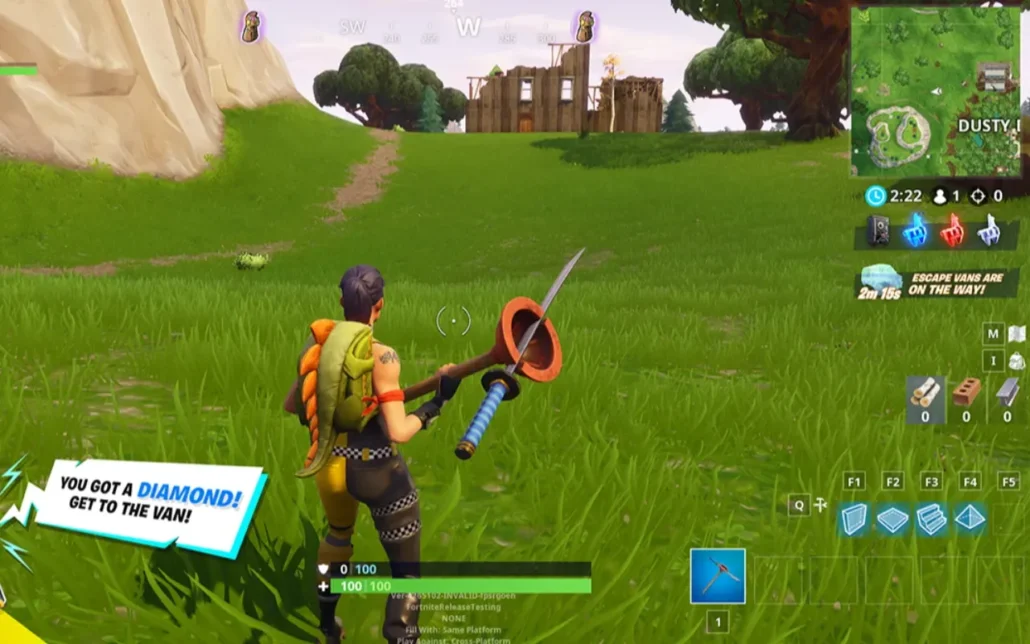
Fortnite is a great example of a game that is easy to navigate. The interface shows clear information, like maps and health. This makes it simple for players to know what’s happening at all times. It also has settings that let players change controls, making the game more accessible to everyone.
Note: Make sure the game is easy to understand for all players, no matter their skill level.
Conclusion
The UI/UX design pipeline for game interfaces is an essential framework for creating intuitive player experiences. From research and prototyping to post-launch updates, each stage ensures that the final product aligns with both user expectations and the game’s goals. By utilizing the right tools and best practices, designers can create game interfaces that truly enhance gameplay.