3D computer graphics created new careers that didn’t exist before the 90s. Creating 3D models of objects, characters and environments is an example of such career. 3D models are the primary form of art used in creative projects such as 3D games and animations. A 3D modeller is an artist who uses 3D design programs to create these models. In this post, we will explore the 3D modelling career path and the required skills for a 3D modeller.


Need Game Art Services?
Visit our Game Art Service page to see how we can help bring your ideas to life!
Responsibilities of a 3D Modeler
Creating 3D Models
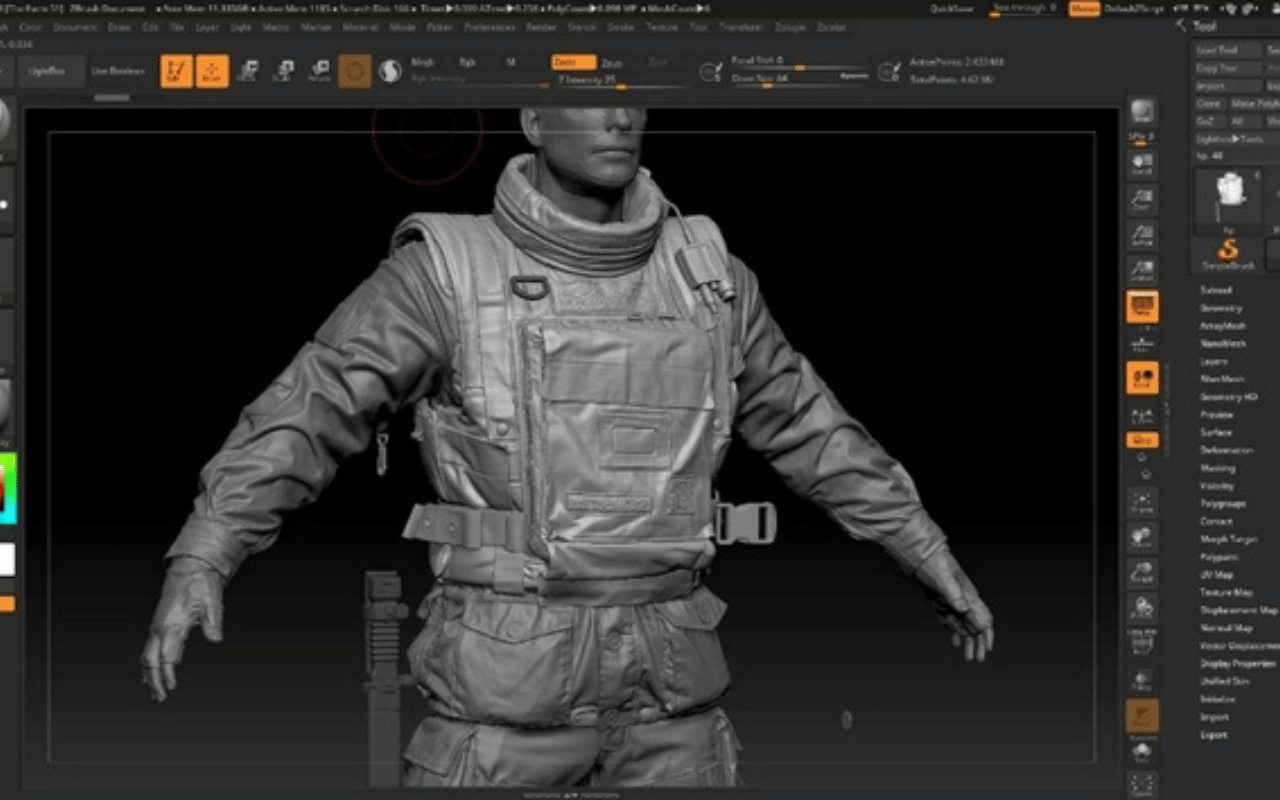
3D modelers are responsible for creating 3D models. They should understand the style a project is aiming for using concept art or reference images that are given to them by lead artists, art directors or clients. They decide which workflow works best for different models and use 3D modelling programs to create them.
Adjusting Models for Specific Use
3D models should require different characteristics and functionalities from one project to another. 3D modellers should work with other artists like animators and technical artists to adjust models according to the specific needs of a project. For instance, 3D models often need some topology tweaks for easier rigging and animation.
Optimizing models
Optimizing 3D models based on the type of project they are going to be used in is an important responsibility of a 3D modeller. Games have different requirements for 3D models compared to animation. Game models should have a lower polygon count to perform better in real-time, while using high-polygon models in animation is standard, as the final rendering process is often lengthy.
Essential Skills for a 3D Modeler
3D modelling is a technical field that demands technical and interpersonal skills at the same time. In this section, we will explore the most essential skills required for a 3D modeller.
Communication Skills
3D models are not something only one person works with. From the initial stages of creating a 3D model to animation and final rendering, different artists work on 3D models. Ensuring that these models meet the specifications requested by different production teams requires constant communication between 3D modellers and other artists. Thus, effective communication skills are essential for a 3D modeller.
Technical Skills
3D modellers use software like Blender, Maya, and 3ds Max to create 3D models. Proficiency in these programs is essential as they are the tools of the trade. A good understanding of human anatomy is also necessary for 3D modellers who are primarily focused on creating 3D characters and creatures. The ability to think and visualize objects and shapes in 3D is also crucial for 3D modelers.
As we will explain later in the article, the 3D modelling pipeline includes more than just creating the models. There are some other tasks like texturing, rigging and UV mapping that are often handled by other specialized artists. However, a working knowledge of these tasks allows 3D modellers to work independently in smaller studios that can’t afford to hire many artists.
Attention to Detail
Creating polished and high-quality models requires great attention to detail. 3D modellers should analyze models meticulously to ensure their geometry and topology are correct and clean before passing them to rigging artists. Small mistakes in the modelling process can lead to models deforming unnaturally in rigging animation.
The 3D Modeling Process
Defining the Workflow
The 3D modelling process starts with defining the workflow. Important decisions like whether models should be created using hard-surface modeling or sculpting are made at this stage. Lead artists and art directors collaborate with 3D modelers to determine the workflow and art style that matches the requirements of the project.
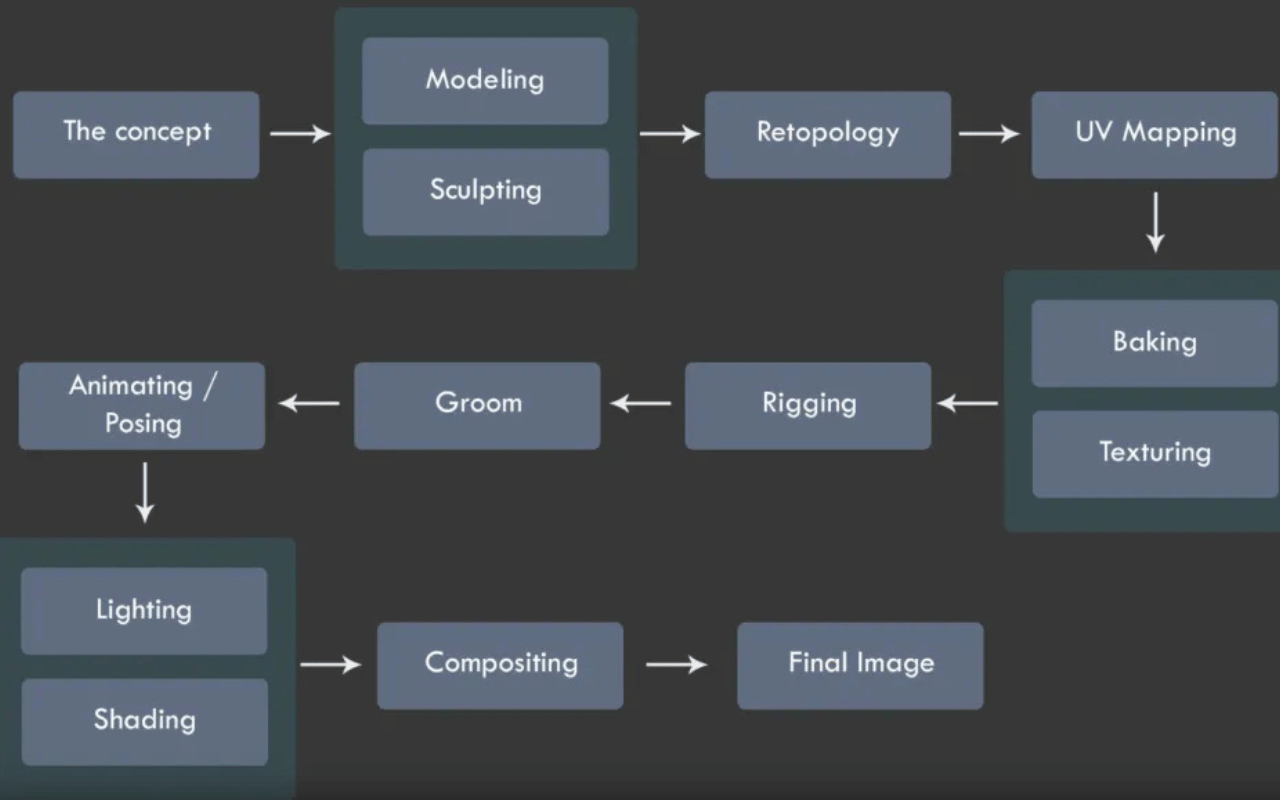
Modeling
In this stage, 3D modellers start the modelling process using 3D modeling software like Maya and Blender. They use primitive shapes to block out the main parts of 3D models and then manipulate their geometry by editing the models’ points and edges to create the desired shapes. This method is best suited for hard-surface models such as buildings, cars, mechanical objects, and weapons.
Read More: What Are the Top 3D Modeling Techniques?
Sculpting
Organic models like characters and creatures are easier to create using sculpting tools. The sculpting process is similar to making a real-world sculpture. Sculpting tools allow 3D artists to manipulate 3D objects and mould them into desired shapes. This process is suitable for adding intricate details that are difficult to create using hard-surface modelling techniques.
UV Mapping and Texturing
The next step in the 3D modelling process is applying textures and materials to models. Textures are 2D images wrapped around models to add colour. Since 3D models are made of hundreds or thousands of small polygons, their surfaces are laid out flat using a process called UV Mapping so that a texture, which is 2D images, can be adjusted accordingly.
Industry Applications
3D models are commodities that fuel creative projects. From video games and animations to product modelling and architectural visualisations, they are found in many industries. Let’s explore various use cases of 3D models.
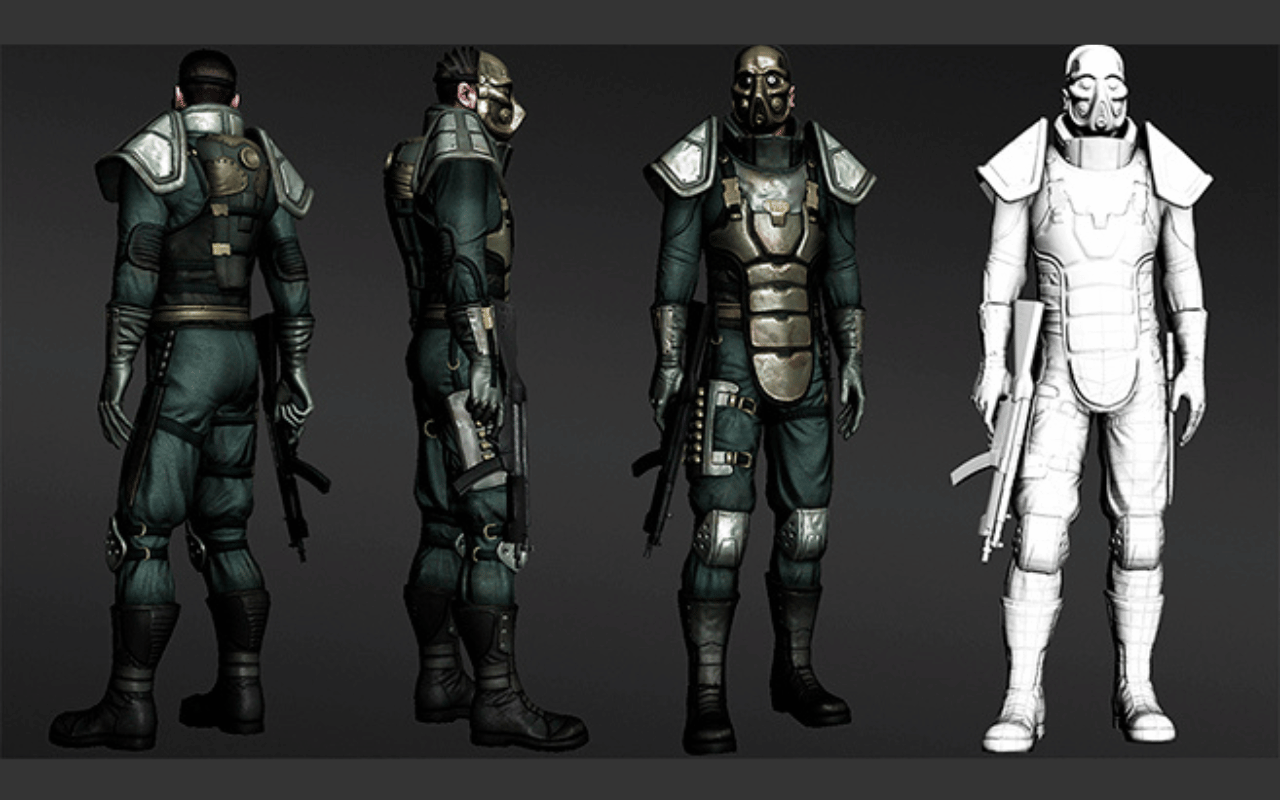
3D Models in Video Games
3D modeling services are used extensively in video games. Almost all assets used in 3D games are created using 3D modelling. Characters, environments, weapons, cars, and props are all examples of game assets created using 3D modelling.
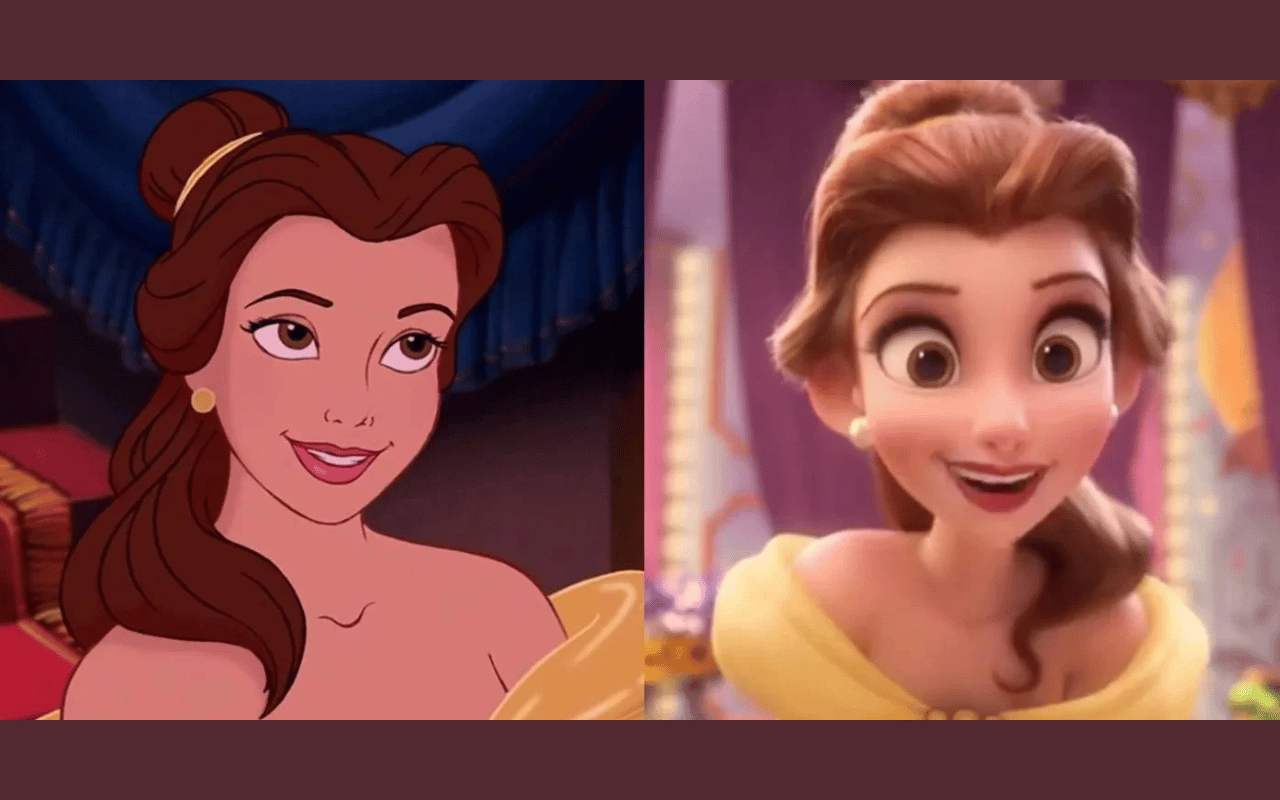
3D Animation
3D animation is another field in which 3D models are featured extensively. Nearly every object and character that we see in a 3D animated film is a 3D model. Feature animation, animated commercials, and motion graphics all utilise 3D models.

Product Visualizations
Product visualisations are 3D representations of real-world products. They are virtual replicas of the actual product used for marketing and demonstration purposes. Product visualisations are a popular form of advertising because of their engaging visuals.
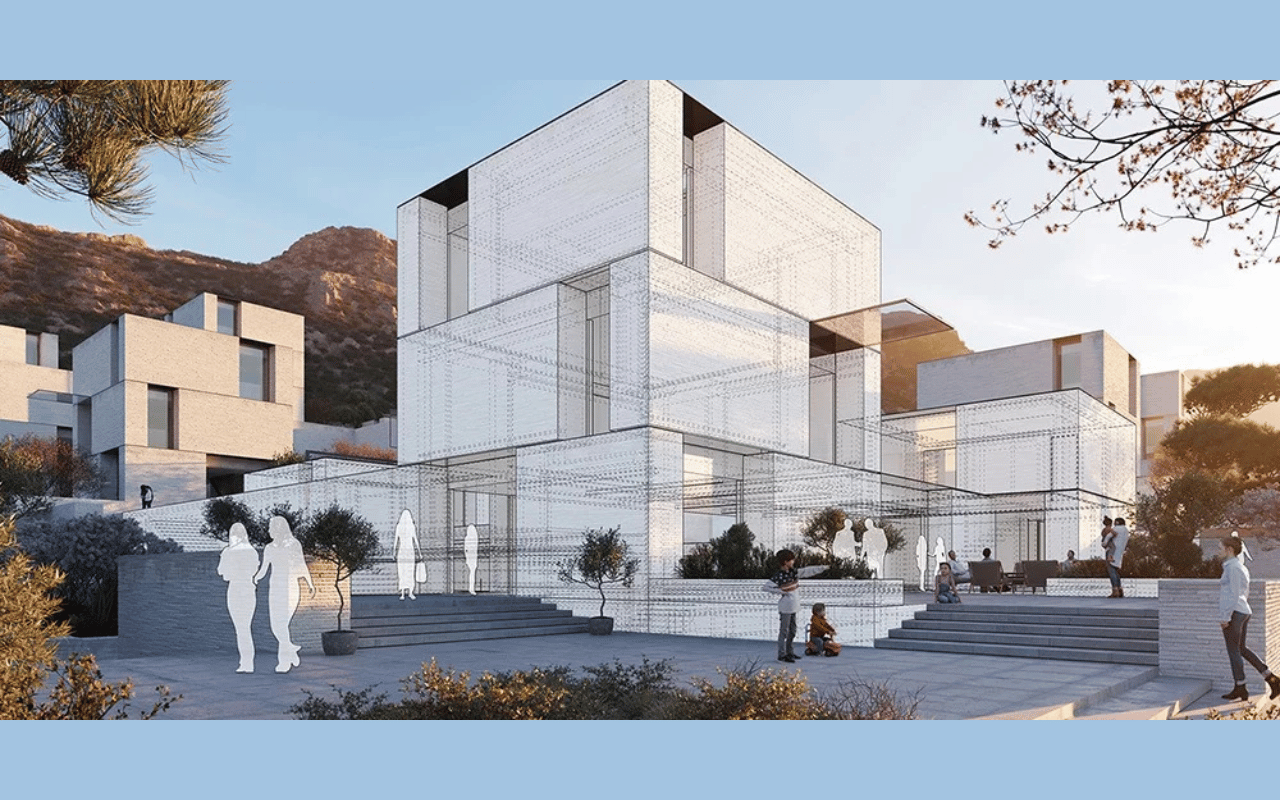
Architectural Visualizations
The architecture industry relies on 3D models for architectural visualisations. Architects create 3D environments using modelling techniques to showcase their designs. They make previews for internal and exterior designs, real-estate designs and more.
Simulations
Computer simulations are used in many industries. Mechanical design companies, construction firms, biology research labs and medical institutions are among many industries that use 3D models to create various scientific simulations.
3D Modeling Tools and Software
3D models can be created using various software such as Blender, Maya, and 3ds Max, Zbrush, and Cinema 4D. Each software has its own advantages. In this section, we will explore major software used for 3D modelling.
Maya
Maya is the industry standard program in 3D animation. It is a powerhouse animation program that has long been used by animation studios all over the world. Maya comes with all the necessary tools typically needed for 3D modeling. Maya’s distinct strength is its powerful character animation features.
Blender
Blender is a free and open-source 3D animation program that has become massively popular in the past few years. Its unique modeling capabilities and powerful keyboard shortcuts that allow faster creation of 3D models are favored by many 3D modelers. Blender also comes with complete sculpting tools that are on par with industry-standard sculpting programs like Zbrush.
Read More: Maya vs. Blender
3ds Max
3ds Max is a 3D animation and modelling program released in 1996. 3ds Max is known for its powerful modelling tools and plugins that allow automation of time-consuming tasks. 3ds Max is popular among architectural designers due to its ability to handle large scenes and its variety of modelling tools for applying intricate details.
3D Modeling Career Path
The 3D modeling career path typically starts with a junior 3D modeler position in the game, animation or visual effects studios. 3D modelers can take two distinct career routes. They can either become an expert in narrow fields like modeling and texturing or acquire a broader set of skills that prepares them for general positions like directing.
Getting experienced and skilled in one or two fields can lead to senior artist or lead artist positions while becoming familiar with other skills like animation, visual effects, compositing, and leadership prepares an artist for roles like art director or creative director that require a holistic view of the entire pipeline.
Recent Trends in 3D Modeling
From the advent of 3D graphics in the 90s until now, the styles and looks of 3D models have gone through many changes. Usually with the advancements in software and hardware, 3D models improve and look more realistic and polished. However, the high costs of creating top-notch 3D models made some studios look for budget-friendly ways to create 3D models.
Low Poly Models
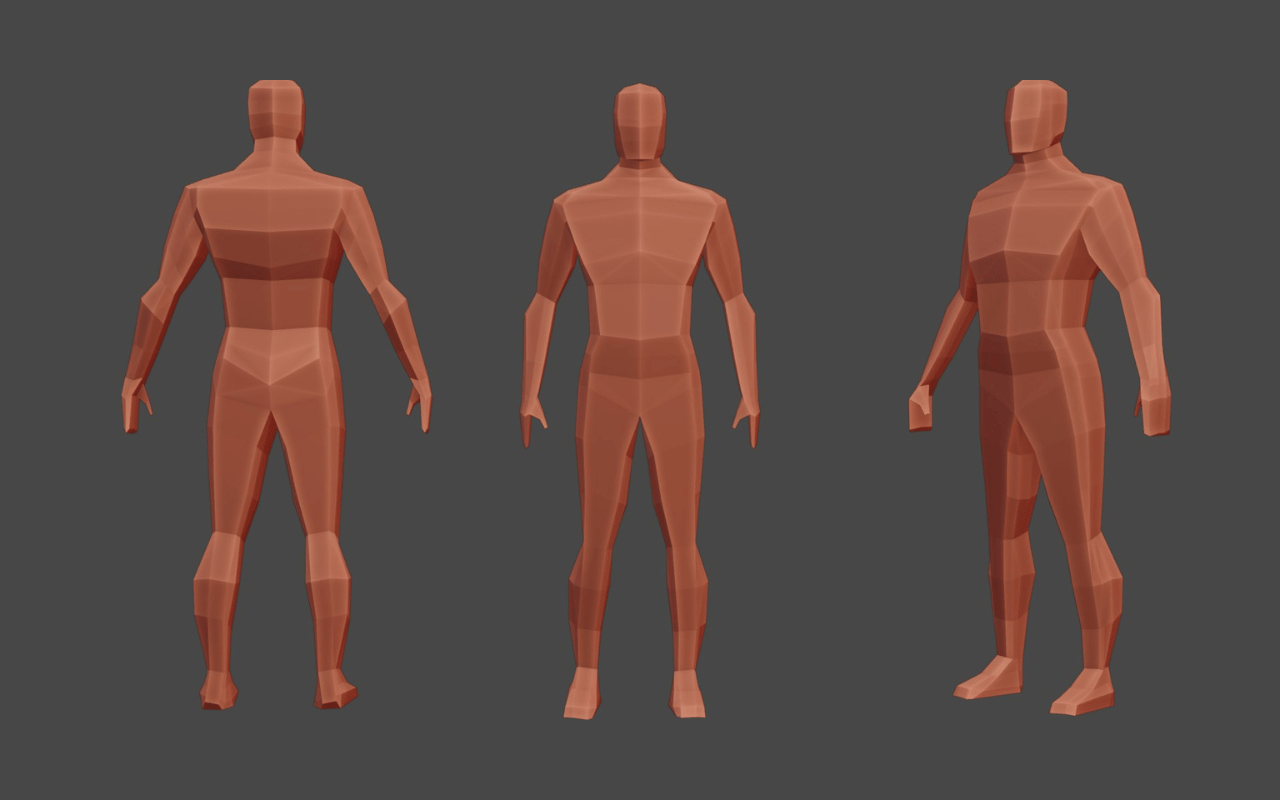
Low poly models are 3D models that come with a lower polygon count. They consist of blocky shapes with fewer details. Low poly models are often used in indie and low-budget games because they can be created faster.Low-poly models are considered key resources for bringing many games to life.
3D Models with 2D Art Style
High-quality realistic 3D rendering is a time-consuming and costly process that requires thousands of GPUs for a feature-length animated video. Additionally, the 2D art style looks fascinating when blended with 3D characters. Thus, many animation studios in recent years have opted to combine the perks of 3D animation and 2D art. Shows like Arcane and feature animation like “Spider-Man: Across the Spider-Verse” used this style and achieved massive success.
Read More: How to Make 2D Art Look 3D?
Final Words
3D modelling is an exciting career that suits creative individuals who like to create art using computers. There are many job opportunities for artists who can prove their technical ability alongside a creative vision. 3D modelling can be a rewarding career if approached with passion and perseverance. If you think this description matches you, you might consider looking into the fascinating world of 3D art.








