To become an excellent animation modeler, master 3D modeling software, study anatomy and form, and practice creating diverse models with proper topology for animation. 3D modeling is the process of creating three-dimensional digital representations of objects or surfaces using specialized software. In the world of animated films and video games, modelers bring characters, props, and environments to 3D life. Developing excellent modeling skills opens up career opportunities across visual effects, game studios and more by enabling you to craft the assets that set the stage. This guide covers must-have abilities and expertise to build, texture intricately detailed models ready for the animation pipeline.

Need 3D Animation Services?
Visit our 3D Animation Service page to see how we can help bring your ideas to life!
Who Is an Animation Modeler?
Animation modelers are digital sculptors who bring characters, creatures, props, and environments to 3D life, starting from concept art. They interpret 2D drawings and designs to construct meticulously detailed 3D assets and scenery that become the foundation for animated films, video games, VFX, and beyond.
This work demands both artistic vision to evolve ambiguous creative jumping-off points as well as mathematical rigor to build functional models that integrate into production pipelines. Modelers must internalize spatial relationships and real-world scale. Their expertise breathes tangible form into pre-production blueprints, enabling directors to achieve bold visual visions.
These digital sculptors operate as technical and creative conduits, translating ideas into 3D geometry. With patience and intense curiosity, modelers craft the meticulous building blocks that empower animated storytelling.
What Is the Role of a 3D Modeler?
As mentioned before, 3D modelers have tough jobs and different responsibilities. Here is listed their role and responsibilities in this industry:
- Creating realistic organic and hard surface computer-generated models in line with instructions and references.
- Provide modeling feedback on concept viability
- Translate abstract concepts into appealing photo-real or stylized 3D assets
- Texture and shader models themselves
- Presenting work for progress evaluations and approval in a turntable-style setting with suitable lighting (including scale reference)
- Ensuring UV mapping and polygonal subdivision uniformity
- Construct UV layouts for texturers
- Facilitating the production of photo-realistic texture maps with high-quality
- Continuously optimize big scenes technically
- Create “hold out” geo, also known as Match-Move geo, which downstream departments like Lighting and FX used to produce more realistic results even if it isn’t always visible in the final render.
- Evaluate model deformations with riggers
What Skills Should a 3D Modeler Have?
Depending on the roles and responsibilities mentioned above in a 3D modeling company, a modeler should have several or all skills as follows:
- Sculpting Technique: The sensitivity to sculpt forms like virtual clay, establishing proper anatomy and proportions. An intuitive sense of shape, weight and depth is mandatory. And knowledge of the differences between modeling and sculpting.
- Topology Flow: Laying out mesh density, edge loops and polygons to enable organic articulation and natural deformations during animation. Ensuring proper pole vectors and edge flow.
- Proportions and Scale: Keen observation skills to recreate and construct elements at precise real-world dimensions, keeping characters, environments and objects true to source material visually. Spatial recognition abilities are huge assets.
- Technical Rigor: Building scale references, optimizing polygons for efficiency, rigging knowledge, assembling multipiece models, and constructing holdout geometry for effects prove technical mettle.
- Strong Knowledge of Anatomy: Understanding the science behind human anatomy and how figures and objects appear.
- Excellent Communication Skills: Able to collaborate with various people in the 3D animation pipeline to solve issues and realize the director’s vision.
- Knowing the Skills of Animators and Animation Software: As well as having a complete understanding of all elements of the animation production process and animation software, knowing how to work with related 3d modeling software is essential to understanding animation pipelines.
- Watching Animations: Have a passion for the medium and the business when you watch animations.
- Modeling Skills: Strong knowledge of modeling techniques and skills for polygon subdivision.
- UV Layout: Experience with a highly effective UDIM workflow, UV layout, and 3D texturing is necessary.
Top-Tier Portfolio Must-Haves
Modelers seeking to ascend into lead roles balance versatility and precision by highlighting diverse original models:
- Creatures: Quadrupeds, fantasy beasts, alien lifeforms
- Characters: Faces, hands, clothed bodies, hair
- Environments: Landscapes, architecture, furnishings
- Vehicles: Cars, aircraft, watercraft, sci-fi craft
- Props: Weapons, gadgets, accessories
With such breadth, art directors gain confidence in assigning you complex, mission-critical modeling tasks.

What Does a Character Modeler Do?
Character modelers build 3D characters for movies and incorporate them into live-action. Their work is primarily done in post-production, but pre-production sketches and concept art will be generated as part of the production design for the movie or television show. A 3D character modeling company conceives and produces the character art used during the creation of animated films and television shows.
They collaborate closely with the creative teams of writers, directors, and designers to bring the characters to life. Complex character development and artistic ability are needed to generate emotion through drawn images.
They collaborate closely with the technical and creative departments to develop the game’s visual quality and keep a steady sense of character design. Players increasingly demand high-standard graphics in the competitive gaming market. Thus, it is up to the character modeler to deliver the overall artistic quality of the game. The procedures are the same as in gaming, but interactive elements or behaviors won’t be included since a film has a linear structure.
Read More: How Long Does it Take to Make a 3D Model?
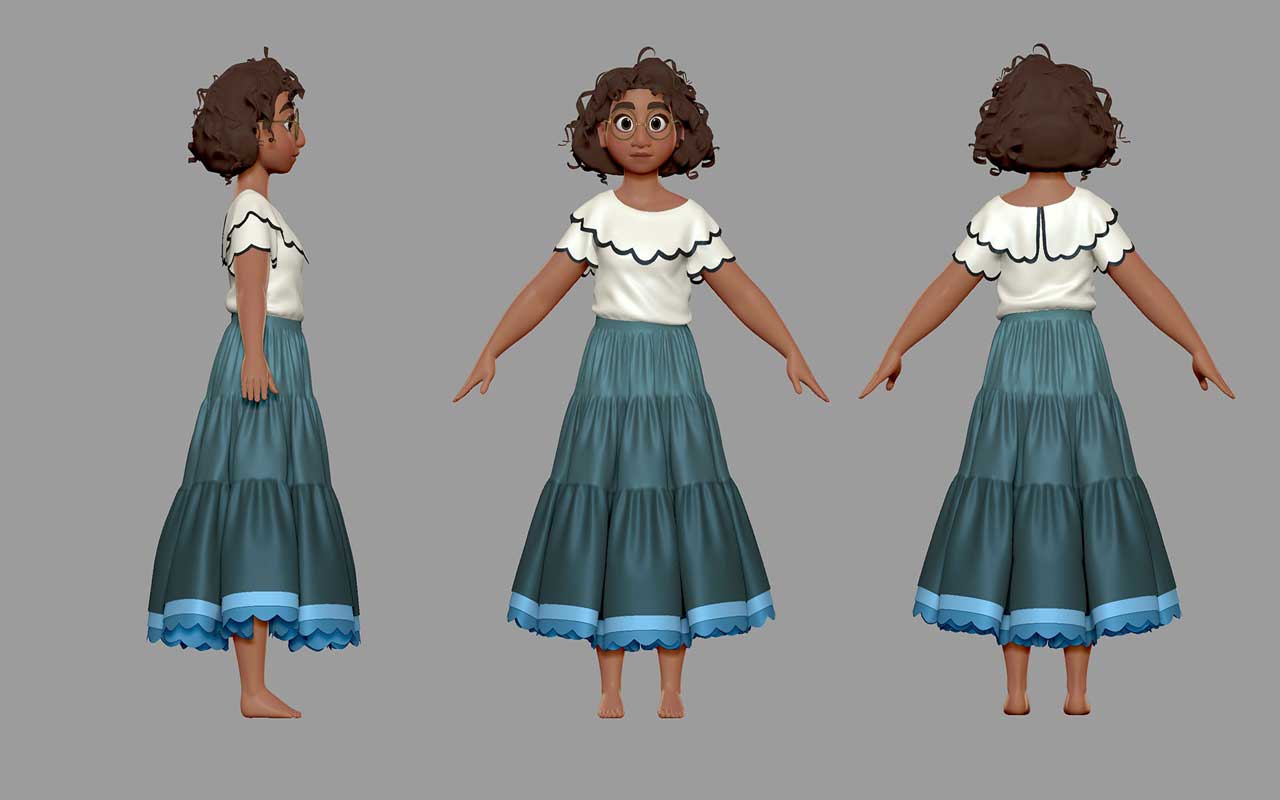
Types of Modeling
At a basic level, modelers construct two key types of digital assets:
Organic Models: Characters, creatures, vegetation, and other natural elements with smooth, flowing shapes. Requires a nuanced 3D sculpting ability.
Hard Surface Models: Mechanical objects, buildings, furniture, vehicles and manufactured items with precise angles and measured topology. Hard surface modeling needs acute technical precision.
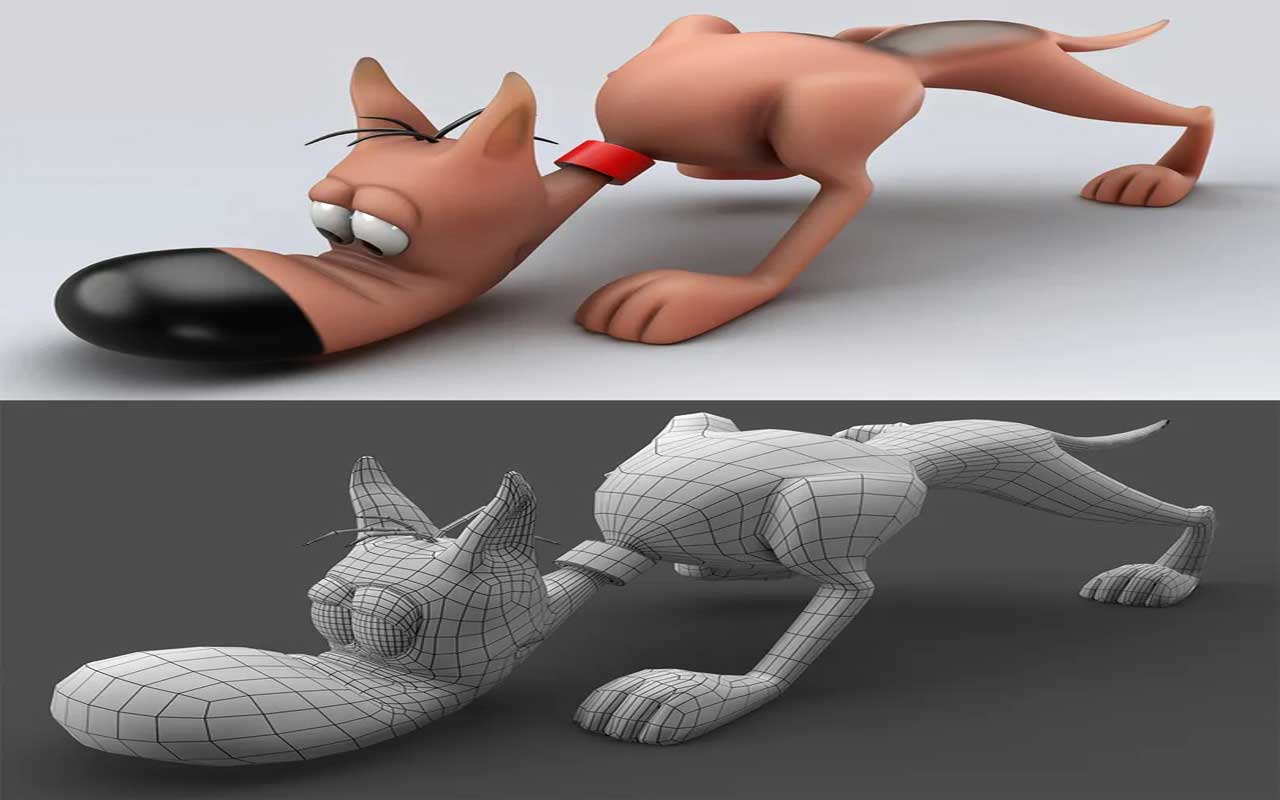

Is 3D Modeling Hard?
Animation and bio-visualization are two fields that benefit from the rapidly expanding field of 3D modeling. But is it challenging to learn 3D modeling? The fundamentals of 3D modeling are easy to learn. Due to its complexity and variety of possible approaches, acquiring this skill is a little bit tough. For the average person, acquiring any talent in the CG world is incredibly difficult. This might be because it seems simpler than it is. Moving objects around in a 3D program appears simple, and we all have creative ideas for things we want to make. So one of the things we need the most is imagination, as explained below.
Imagination
You need to create a visual record of the environment you live in; it’s not simply about imagination. Any topic that appeals to you should be adequately examined. You must understand the various wing designs as well as the concepts governing how and where their bolts are placed if you want to model airplanes. You are fascinated by the history of an object’s design and the purposes of each of its parts.
Understanding how wood is bent in this way or how it behaves when cut may help you add the necessary elements to something as basic as a barrel. At this stage, many people fail! To successfully produce anything that appears authentic and appealing, patience, practice, and research are required. ” Intrinsic Motivation” is the term used for this, and It signifies that you don’t need the motivation to practice. You love it so much and are so driven that it is easy for you to go back and get back at it consistently. Different skills are also required.
Combination of Different Skills
You need to acquire different skills to be a successful 3D modeler. Those skills were mentioned before. To make it short, a combination of mathematics, art and design skills, related software, and scripting is needed.
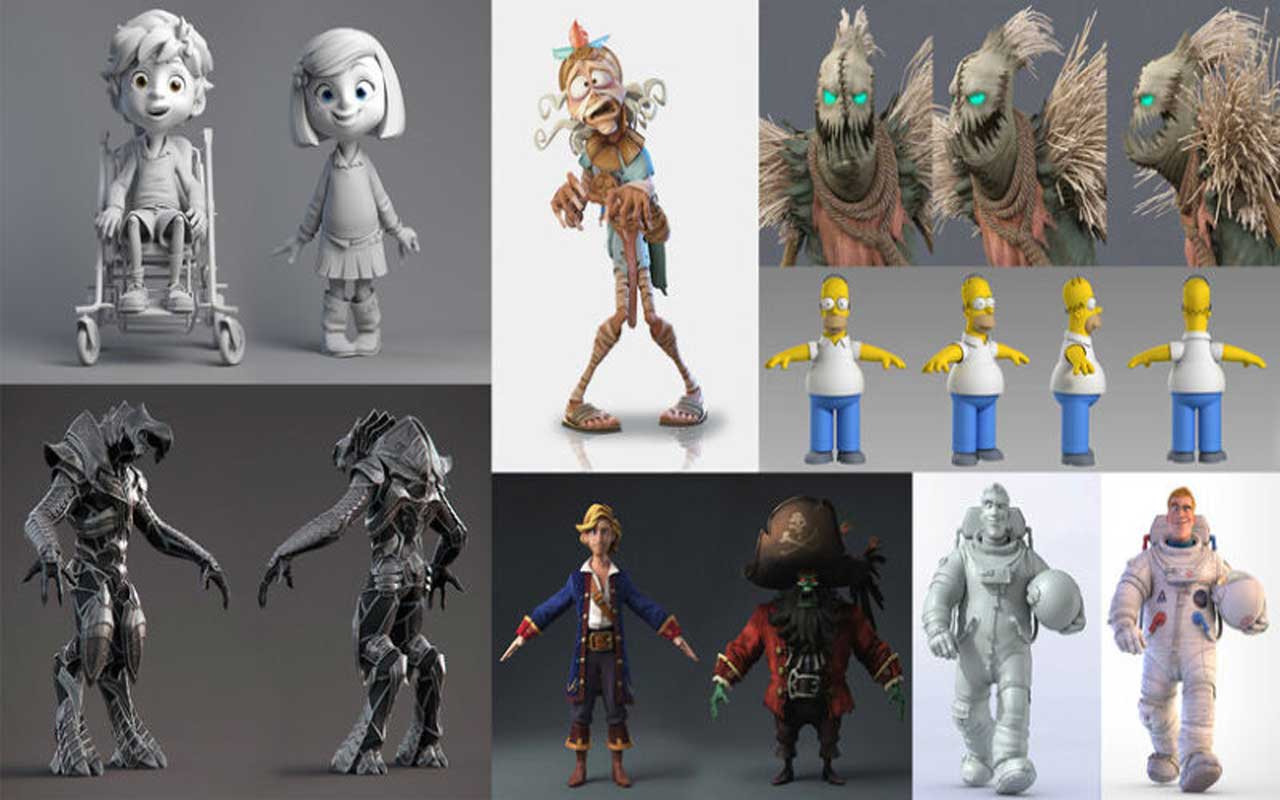

Should I Learn 2D Art Before 3D Modeling?
In a nutshell, the answer is no. You do not necessarily need such talents to find work or work as a freelance 3D modeler. If you want to understand the principles of perspective, color, shading, etc. better, then having experience with expert hand painting or sketching would undoubtedly be helpful. However, it won’t be a necessary skill; rather, it will be a bonus. Lighting, rendering, and compositing are what you need to learn.
In addition, if working at a 3D art studio is your dream job, you probably need to become involved in a wide range of activities your agency provides. For instance, your company might require you to perform a 3D scan cleanup once or twice. Thus, you’ll need to be an expert in this field, at the very least, to deliver a high-quality and polished 3D model. Animation is another area where you could be asked to improve if the studio is new.
The principles of perspective, color, and shading will unquestionably provide a reasonable basis on which you can build further layers of 3D modeling expertise. In any case, all experts use references. The critical distinction between 2D and 3D art is the requirement to activate spatial thinking to go above and beyond and add additional depth to your artwork. Some professionals see 3D modeling as more of a technical activity than a creative one.
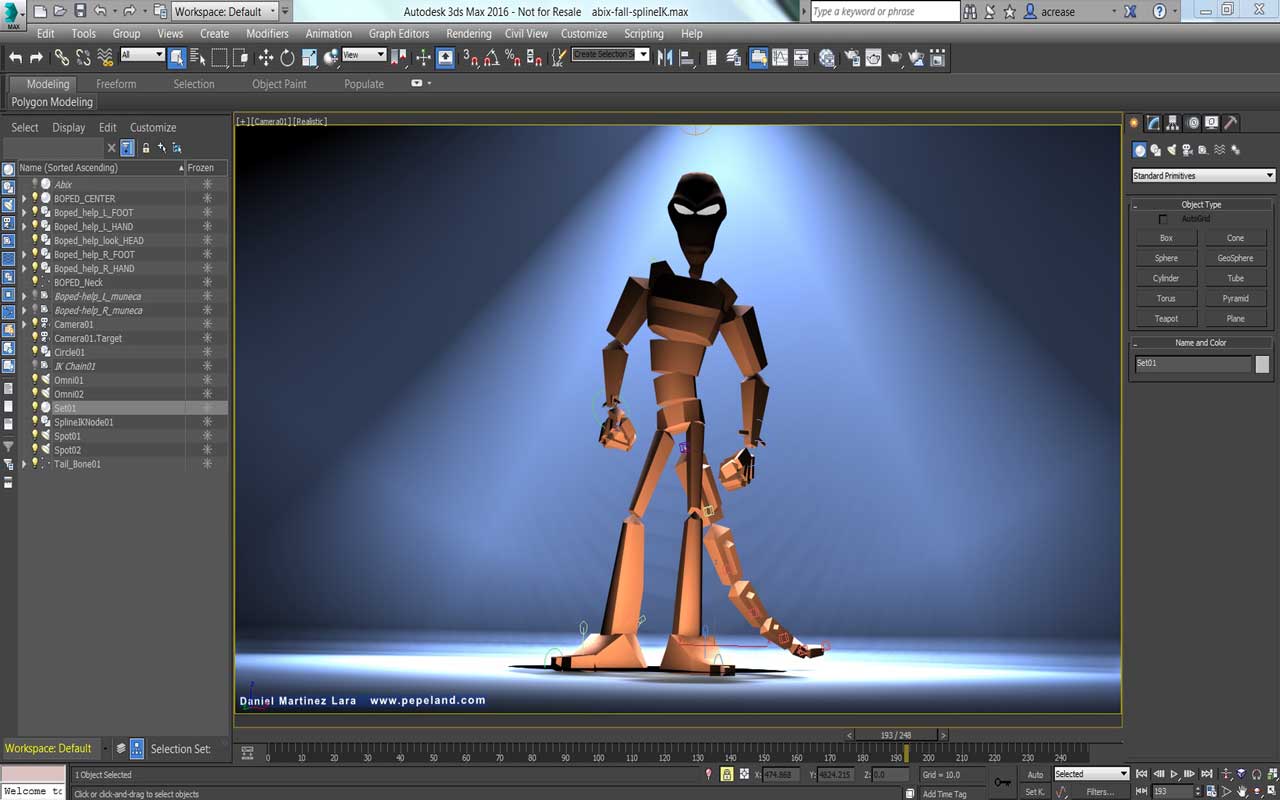
To Conclude
Although learning 3D modeling may be difficult for you, don’t let that stop you. The adventure is fun, and you’ll learn new ideas about the world. You can start working on your projects, contribute to the creation of video games, and create three-dimensional models for almost any industry once you have mastered all the necessary techniques and have gained a deep understanding of the theory behind 3D art. 3D art can be used in various contexts, including filmmaking, game development, cartoons, commercials, the metaverse, and more.