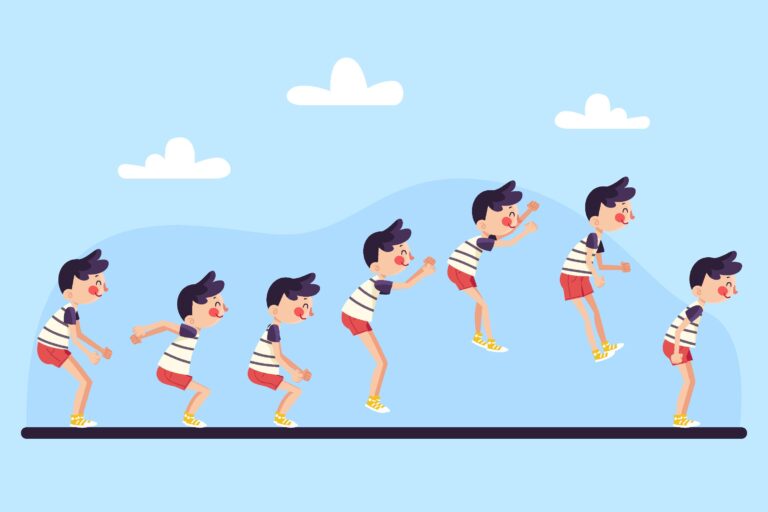
Keyframes are one of the most fundamental concepts in animation. With some slight differences, the term “keyframe” almost refers to the same idea in both traditional and digital animation.
At a basic level, keyframes are the frames where the start and the end of the animation are drawn or recorded.
There are several types of animation that are made with the use of the same concept.
In this article, we will examine what frames and keyframes are, besides exploring the types of animation created using this concept.

Need Animation Services?
Visit our Animation Service page to see how we can help bring your ideas to life!
Types of Keyframes
Some animation software comes with options for changing keyframe behaviors.
As we explained earlier, keyframes are used to transition between two states over time.
- This transition can follow a linear pace and remain constant between two keyframes. “Linear Interpolation Keyframe” is the term used to explain this type of keyframe.
- Another type of keyframe that is used in animation is a Bezier Interpolation Keyframe. Bezier keyframes allow animators to change how quickly an object’s attributes change.
This type of keyframe is used heavily in every type of animation, including motion graphics and character movements.
Using Bezier keyframes, animators adjust how fast an object moves or stops to create the illusion of weight and other physical attributes.
These keyframes do not always have the same names in animation software.
Some animation software, like Maya or Blender, comes with graph editors where animators manipulate keyframe transitions, while other software, like Adobe After Effects, relies on changing keyframe types in the main timeline to change keyframe types.
What Is Keyframe Animation?
How do animators create smooth, lifelike motion in films, games, and digital ads? Keyframe animation is the technique where animators define critical moments, or keyframes, and software fills in the transitions to finalize a fluid movement.
The main aspects of keyframe animation are:
- Defining Motion: Keyframes mark the start and end of actions, like a character jumping or a logo spinning.
- Automation: Tweening generates in-between frames, saving time while ensuring smooth transitions.
- Versatility: Used in 2D Animation, 3D Animation, and Motion Design, from films to mobile games.
By balancing manual control with automated interpolation, keyframe animation is a cornerstone of the animation timeline, enabling creators to craft dynamic visuals in Visual Effects (VFX) and beyond.
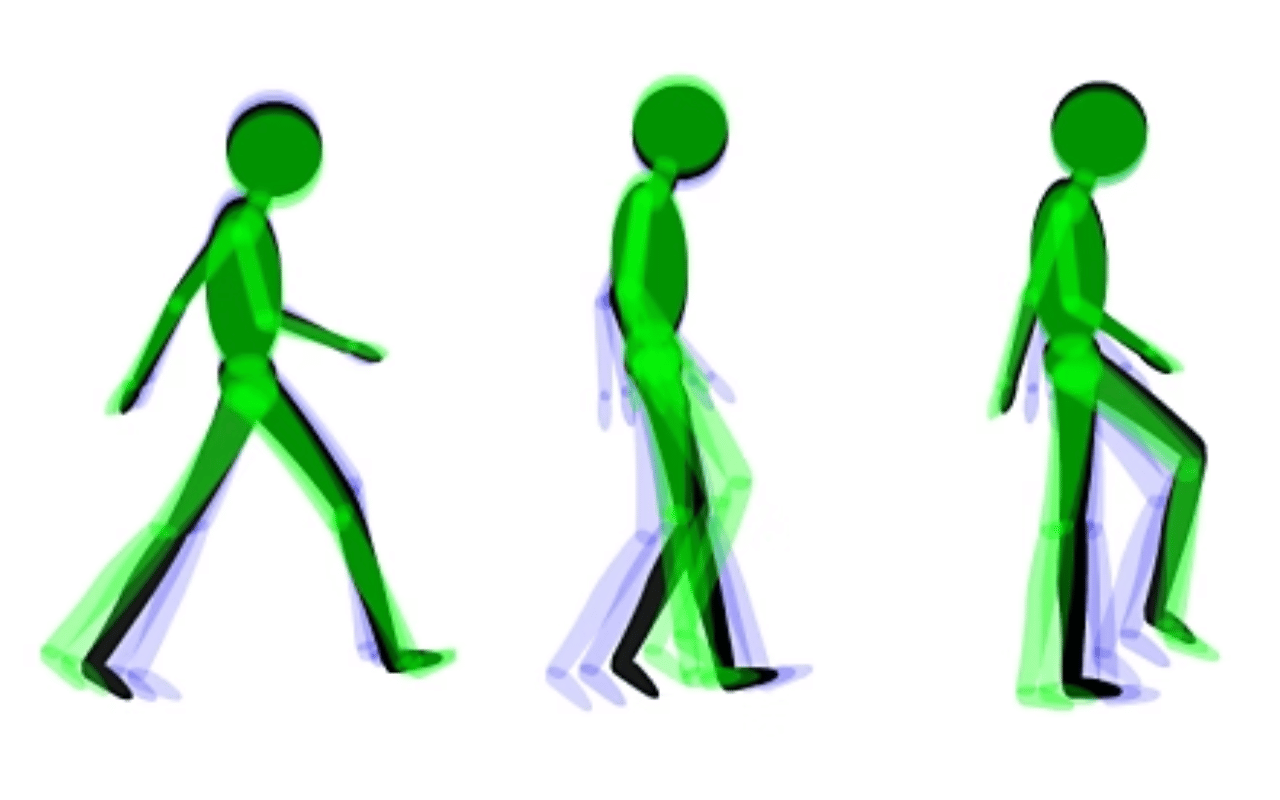
The Core Techniques and Terms of Keyframe Animation
Keyframe animation revolves around setting keyframes, specific frames that define an object’s state, and letting software handle the transitions.
Understanding keyframe animation tips, core techniques, and terms is essential for grasping the keyframe animation definition and exploiting the method effectively.
Key concepts and techniques of “keyframe-ing” include:
- Frames vs. Keyframes:
A frame is a single image in an animation timeline, typically 24–30 frames per second.
A keyframe is a frame where a significant pose or state is set, like a ball at the peak of a bounce. - Tweening: Software generates in-between frames to create smooth motion between keyframes, otherwise known as automating in-betweening.
- Interpolation Types: Linear interpolation creates constant motion; Bezier interpolation allows ease in / ease out for natural acceleration and deceleration.
- Animation Curves: Visualized in a graph editor, curves control how attributes like position or scale change over time, refining timing and spacing.
- Pose-to-Pose Animation: Animators set keyframes for major poses, contrasting with frame-by-frame animation, where every frame is manually drawn.
In practice, animators might set keyframes for a character’s jump: one at the crouch, one at the peak, and one at landing.
Software like Autodesk Maya or Adobe After Effects uses animation curves to interpolate these poses, ensuring fluid motion.
Bezier keyframes add realism by mimicking physical weight, as seen in Spider-Man: Across the Spider-Verse, where characters’ movements feel dynamic.
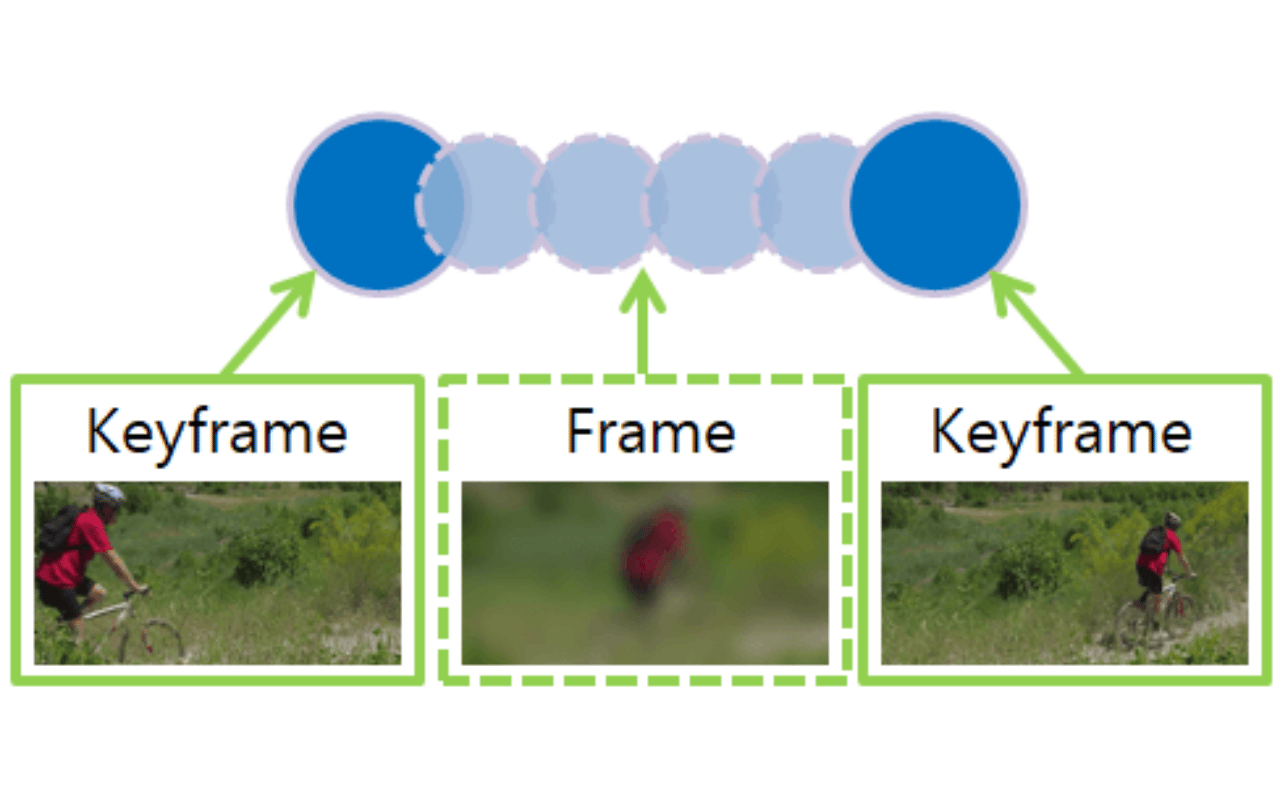
What is the Difference Between a Frame and a Keyframe?
As we briefly discussed, to understand keyframe animation, we need to first know what frames are.
One second in animation is usually split into 24 frames. to animate a one-second shot, you need 24 drawings, one for each frame. Now that we know what a frame is, we need to understand keyframes.
A keyframe, as its name suggests, is a frame on which a key drawing or pose is drawn in frame by frame animation.
Key poses mark the start and the end of an animation. Imagine you want to animate an object falling. Your animation will consist of two keyframes, one when the ball is high in the air and the ending keyframe when the ball hits the ground.
What Are the Types of Keyframe Animation?
If you examine how animation is made, you will soon realize keyframes are used in almost every type of animation. However, spotting them at first glance might not be obvious. Let’s explore how various types of animation rely on the concept of keyframes.
1. Traditional Keyframe Animation
Animation was traditionally created using physical materials such as pen, paper, paint, and celluloid sheets. Lead animators would draw key poses for an animated shot, and then other animators, referred to as in-betweener, would draw the frames between these keyframes.
That is actually where the term keyframe animation has come from. Each frame was then photographed by a camera and turned into a film.
But how do keyframes and in-between frames in traditional animation differ? Key frames are the points in animation when more important movement features happen.
Usually, the beginning and the end of an action are considered key frames. In-betweens are the frames that create the smooth transition between these key starting and ending poses.
2. Stop Motion Keyframe Animation
Stop motion is a type of animation made using physical puppets that are adjusted in various poses in front of cameras.
For each frame in stop motion animation, physical puppets or objects are set in desired poses, photographed, and moved for the next frame.
Unlike traditional animation, in which in-between frames are considered less important than keyframes, stop motion animators physically manipulate all objects for every single frame.
Stop motion animation is an animation technique used in many types of animations like Claymation, object animation, LEGO animation, Silhouette animation, and cutout animation.
The primary difference between these types of animation is the use of different materials and objects to create animation.
3. Motion Graphics
Motion graphics is a type of animation that uses the same keyframing concept as 2D and 3D keyframe animation.
What makes motion graphics different from these types is the emphasis on creating visually appealing motions rather than detailed character animation.
Motion graphics rely heavily on dynamic animations applied to simple graphics and texts, transforming them into new eye-catching shapes to attract users’ attention and convey ideas.
Like other forms of keyframe animations, these movements and transitions are created by assigning keyframes to objects’ attributes.
Motion graphics can be in 2D and 3D. Usually, Adobe After Effects is used to create 2D motion graphics, and Cinema 4D is a popular choice for 3D motion graphics.
4. Digital Keyframe Animation
Digital keyframe animation is created using computers.
In this type of animation, keyframes are markers set by animators on animation timelines.
These keyframes record the state in which an entity, such as a character or an object. Like traditional animation, these keyframes mark the beginning and the end of an animation shot; however, what is fundamentally different is the role of computers in generating in-between frames.
Computers move objects or characters between keyframes to create the animation sequence.
Another concept that is crucial to understand is the way computers render images on screens. Computers usually render images 60 times per second or even more, depending on the hardware used, while animation software divides time into seconds made of 24 or 30 frames. These frames from computers and animation software should not be confused with each other.
Nevertheless, digital keyframe animation comes in different forms.
We will provide a brief overview of the primary ways of creating digital keyframe animation next.
2D Digital Keyframe Animation
2D digital keyframe animation is one of the most widely used types of keyframe animation.
In this 2D type of animation, two-dimensional characters or objects are created using vector or bitmap graphics and animated using animation software.
Unlike traditional animation, where a new image had to be drawn for each frame, in 2D digital animation, characters and objects are drawn once and moved over time.
In this type of keyframe animation, characters and objects are given skeletal systems, also known as rigs.
Rigging allows animators to animate different parts of an object independently or with a parent-child relationship with other parts. This facilitates the creation of complex animation behaviors without the need to draw each frame separately.
This type of animation is also known as 2D digital cutout animation.
2D keyframe animation can be created using 2D animation software like Adobe Animate, Toon Boom Harmony, Moho, and Cartoon Animator.
3D Digital Keyframe Animation
3D digital keyframe animation is probably the most popular form of animation created today.
3D animation is created using specialized animation software that provides users with a three-dimensional workspace. This 3D space allows creating objects and characters that have depth, unlike flat 2D characters.
Working in three dimensions allows 3D artists to rotate around an object and manipulate it like a sculptor.
The layout in 3D animation is not that different from that of 2D animation. 3D characters or objects are set in various poses, keyframes are used to record their location, rotation, and scale for a certain frame, and they are moved for the next keyframe, where those attributes are recorded again.
The animation software then fills in the frames between these keyframes with proper location and rotation information for 3D objects.
3D keyframe animation can be created using various software, such as Maya, Blender, 3ds Max, and Cinema 4D.
Where Keyframe Animation Is Used
Keyframe animation is a universal technique, creating motion in diverse industries, from entertainment to interactive media.
Its flexibility and versatile applications make it indispensable for bringing engaging visuals to life.
Primary applications of keyframe animation include:
Film and TV:
- Character Animation: Animates expressive characters in films like Elemental and series like Invincible using 3D Animation for nuanced performances.
- Environmental Effects: Creates dynamic backgrounds, like swirling clouds, using Maya keyframes.
- Hybrid Productions: Combines animation with live-action, as in The Mandalorian, where keyframes animate Baby Yoda’s movements.
Game Animation:
- Character Animation: Animates player characters, using 3D animation in Maya for realistic motion.
- Cutscene Animation: Powers narrative sequences in Star Wars Jedi: Survivor, with keyframes setting dramatic poses in Blender.
- 2D Sprites: Animates sprites in indie games like Hollow Knight: Silksong, using Spine 2D for lightweight rigging.
Visual Effects (VFX)
Keyframe animation enhances VFX in live-action films with animated elements, seamlessly blending digital and real-world footage.
- Creature Animation: Animates creatures in Dune: Part Two, using Maya keyframes for lifelike motion.
- Environmental Effects: Creates effects like explosions in Mission: Impossible – Dead Reckoning Part Two, with keyframes controlling particle dynamics.
- Character Enhancements: Animates digital doubles, as in Avatar: The Way of Water, blending with live actors.
Motion Design
- Brand Animations: Animates logos and intros, like Spotify’s playlist transitions, using Adobe After Effects.
- UI Animations: Enhances app interfaces, such as button transitions in Adobe XD prototypes, with keyframes controlling opacity and scale.
- Social Media Ads: Creates dynamic ads, like Nike’s animated campaigns, using Cinema 4D for 3D effects.
What Information Do Digital Keyframes Store?
In animation software, keyframes can be applied to any attributes that can be changed for a digital object whether they are 2D or 3D.
These attributes can be location, rotation, opacity, scale, color, shape, and various filters such as gradients and light intensity.
To Wrap Up
The concept of keyframes is a crucial concept in animation that has evolved over time. Initially referring to the key drawn poses and later to photographed drawings, and more recently to the recorded states of an object in an animation software. Although people might refer to slightly different concepts when talking about keyframes, the fundamental concept remains the same. It is hard to find animation that does not rely on keyframes to create moving pictures. Keyframes are the backbone of almost every animation we watch. A keyframe is a key that unlocks the door to imagination. A key to the mesmerizing world of animation.