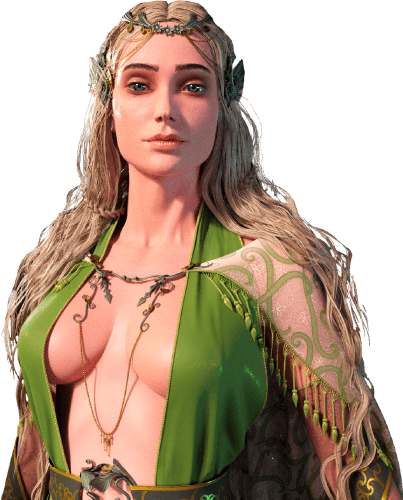
3D art means creating artwork using all three dimensions of width, height, and depth. It is the form of art used to create blockbuster feature animations such as Shrek, Toy Story, Big Hero 6, and Coco.
3D art is a fascinating world that never fails to amuse and amaze the audience. It is a magical tool that makes it possible for us to see imaginary 3D worlds and visualize awe-inspiring phenomena that can never be seen with the naked eye.
Creating 3D art is not an easy feat, though!
In this article, we will explore 3D art, its applications, and various career paths to discover what realms of vision this art form creates!

Need 3D Animation Services?
Visit our 3D Animation Service page to see how we can help bring your ideas to life!
What is 3D Art?
Think of 3D art as building something in a real space with depth, not just drawing it flat.
This art form brings imaginary worlds to life. It lets us see amazing things that are not possible in the real world.
You might wonder what “three-dimensional” really means. Imagine the space around you right now. You can move forward and backward, which is moving in depth. You can go up and down, changing your height. And finally, you can move left and right, moving across the width.
Our eyes and brains naturally understand these three directions, as we see and make sense of the world this way.
3D Art Production Pipeline
Creating 3D art involves several complicated steps, some of which have technical names that might sound confusing at first.
In the following, we have mentioned some of the common steps in creating 3D art, which are similar to 3D animation. Evidently, based on your chosen 3D art format, the stages tend to differ!
3D Modeling
3D modeling is usually the first step in creating 3D art. Understanding 3D modeling is easier with an analogy. Think of a triangle. It has three edges; three connecting points, and one surface enclosed by these edges. If you manipulate the location of points or extend the edges, you get a new triangle with a different shape. 3D modeling is exactly like that. 3D software provides users with some primitive shapes like cubes, pyramids and spheres that have some edges, points, which are called vertices, and surfaces that are called faces. By manipulating and adding edges and vertices, 3D models can be transformed into any shape. In 3D graphics, the term “model” is adopted because computers render shapes on screen according to mathematical models. The coordinates of vertices passed into these models are the parameters that help 3D software define the rendered shape.
3D Sculpting
3D modeling is not the only way to create 3D objects. Another technique, which is used widely to create 3D art, is sculpting, which involves using brushes to mold, deform, and manipulate objects to create new shapes.
3D sculpting is the preferred way to create characters or objects that require higher levels of organic and fluid details, while 3D modeling is better suited for modeling objects that fall under the category of polygonal or hard-surface models such as cars, weapons, walls, and houses.
ZBrush is a software used by many studios for 3D sculpting and 3D modeling.
3D Texturing
The next step in creating 3D art is texturing. Textures are images applied to a surface. When you are done modeling a 3D object, a texture map is needed to apply color and texture to a 3D model.
A texture map is a flat image that defines which images are applied to specific parts of a 3D model. But how can we apply a texture flat image to a 3D object? To do that, we need to UV unwrap the 3D model.
Do you remember unwrapping a cube in school to see that it is made of 6 squares? That is essentially what UV unwrapping does. The software creates a 2D map of all faces that come together to create a 3D model. Finally, texture maps are adjusted manually by 3D artists to match the UV map, so the models are now textured and colored properly.
3D Rigging
The next step in creating 3D art is to give your models bones! A 3D model on its own does not have any form of skeletons. In 3D, the term rigging refers to attaching bones to a model, so certain parts of it can be moved independently or together. That makes it possible for animators to animate models. The term rig, in 3D, is sometimes used to refer to a model that is rigged as well. Rigging is not limited to humanoid or creature 3D models; everything can be rigged in 3D. Think of a kettle you want to animate. You can attach a bone to its handle or lid to animate them. Creating complex rigs for human, animal, or creature characters can sometimes be very complicated.
Animation
After rigging models, animation usually comes next. 3D animation is a laborious task that involves adjusting characters and objects into various poses over time. All animation software has a timeline dedicated to animation. Animators use timelines to set keyframes.
Keyframes are used to set the starting and ending points of an action. Suppose you want a character to throw a ball. To animate that, you need to break down the animation into several key poses and adjust your characters in time accordingly. The animation software is responsible for interpolating objects and characters between these keyframes to create movement. It is worth noting that 3D art does not have to be necessarily animated.
Many forms of 3D art are intended to be static. Stationary game assets, 3D concept art, and architectural designs are some types of 3D art that don’t necessarily need to be animated.
What Software is Used to Create 3D Art?
3D art can be created using special software that provides a 3D scene in a computer. 3D artists can move around this 3D workspace to create 3D objects using all three dimensions explained earlier. They can rotate around objects and manipulate them. Think of a real-world sculptor who can move around its sculpture and deform the sh ape, that is what 3D software makes possible. Autodesk Maya, Blender, 3ds Max, and Cinema 4D are examples of such software.
Read More: Maya vs. Blender
Where Is 3D Art Used?
3D art is used in many different fields, from movies to games and beyond:
3D Animation Industry
This is the most obvious place where 3D art is used a lot.
Commercial animation, like TV ads, heavily relies on 3D art. Scientific and technical demonstrations using 3D animation are also very impressive. Feature films attract millions of viewers and make billions of dollars each year. Animated short films help new filmmakers get noticed.
In this industry, everything is made from 3D art!
3D Art in Games
3D games rely heavily on 3D game art services. From environments, to characters and props, 3D art is prevalent in game development. Creating characters and props for games follows a similar process to the one used for 3D animated movies. However, there are some optimizations specific to game assets. The number of polygons (faces) used in a game model should not be high. Game rigs have some differences from animation rigs as well. Detailed facial rigs and animations are not usually required for game characters in the game art pipeline.
3D Art in Architecture
3D art is also used extensively for architectural purposes. Architects and designers use 3D design software to create visualizations for real estate projects, interior or exterior design previews and architectural walkthroughs.
3D Art in VR And AR
Virtual reality and augmented reality experiences are relatively recent areas where 3D art is used extensively. If you have had the chance to wear a VR glass and experience virtual reality, you know how magical it is to teleport to an imaginary 3D world without leaving your room. 3D art is also used in augmented reality applications.
Augmented reality (AR) combines the real world with 3D art. AR apps overlay 3D objects onto the actual footage received from the phone or glass cameras. Pokémon Go, the massively successful game of 2016, was an AR app made using the Unity engine that filled the world around us with millions of 3D Pokémons.
Creating art for VR and AR is fundamentally the same as video games. These experiences are usually created with 3D game engines as well.
Careers in 3D Art
The world of 3D art offers many exciting career paths.
If you enjoy creating digital worlds and characters, a career as a 3D artist might just be the right fit for you.
1. What a 3D Artist Does!
A 3D artist creates art in digital 3D form. They use computer software to make models, animations, and digital effects for video games, films, and other creative projects.
This job covers the whole design process, from idea to finished product.
You might design how something looks and moves, build a model, create storyboards, and work with marketing and design teams. In some cases, you may also need to consider 3D art outsourcing cost, especially when working with external partners or large-scale productions.
Some common technical skills of this job include:
- 3D Modeling: Creating 3D objects for games, TV, film, real estate, or product design.
- 3D Animation: Making digital animated images, like computer-generated characters and motion graphics.
- 3D Concept Art: Concept artists create computer-generated illustrations and ideas for film, TV, and games, often working with animators.
2. Common 3D Art Specializations!
Within the 3D art field, you can specialize in many roles, especially in film and video games.
Every character, creature, item, and environment starts with a 3D model.
Some common career paths in 3D art include:
- 3D Modeler: Creates 3D objects and models.
- 3D Character Artist: Focuses on digitally building, sculpting, and detailing 3D characters.
- 3D Environment Artist: Creates the digital landscapes and settings.
- Prop Artist (Games): Creates various items and objects for games.
- Texture Artist: Creates and applies textures to 3D models.
- Lighting Artist: Works on the final look and feel of assets, including shading and lighting.
- 3D Layout Artist: Arranges elements within a 3D scene.
- Archviz Artist: Specializes in architectural visualizations.
Conclusion
To wrap up, 3D art is a complicated and fascinating form of art that requires technical expertise as well as artistic taste. Creating 3D art is a complicated process involving multiple technical steps using various software, but it is absolutely worth it. Because It makes it possible to take the audience to the edges of imagination and let them experience something that would never be possible without 3D art.