The 3D animation production is a challenging and complex process of creating a 3D animation. It has various steps: animation tools (software), resources, machines (hardware), and people.
In this article, we’re going to take a look at the 3D animation pipeline and find out, how is 3d animation made. Remember that the term “Pipeline” is not exclusive to the animation industry.

Need 3D Animation Services?
Visit our 3D Animation Service page to see how we can help bring your ideas to life!
Key Components of the 3D Animation Pipeline
The question is, how many step processes for creating a 3d animation are required?
Let’s take a look at three main stages and how to make a 3D animation:
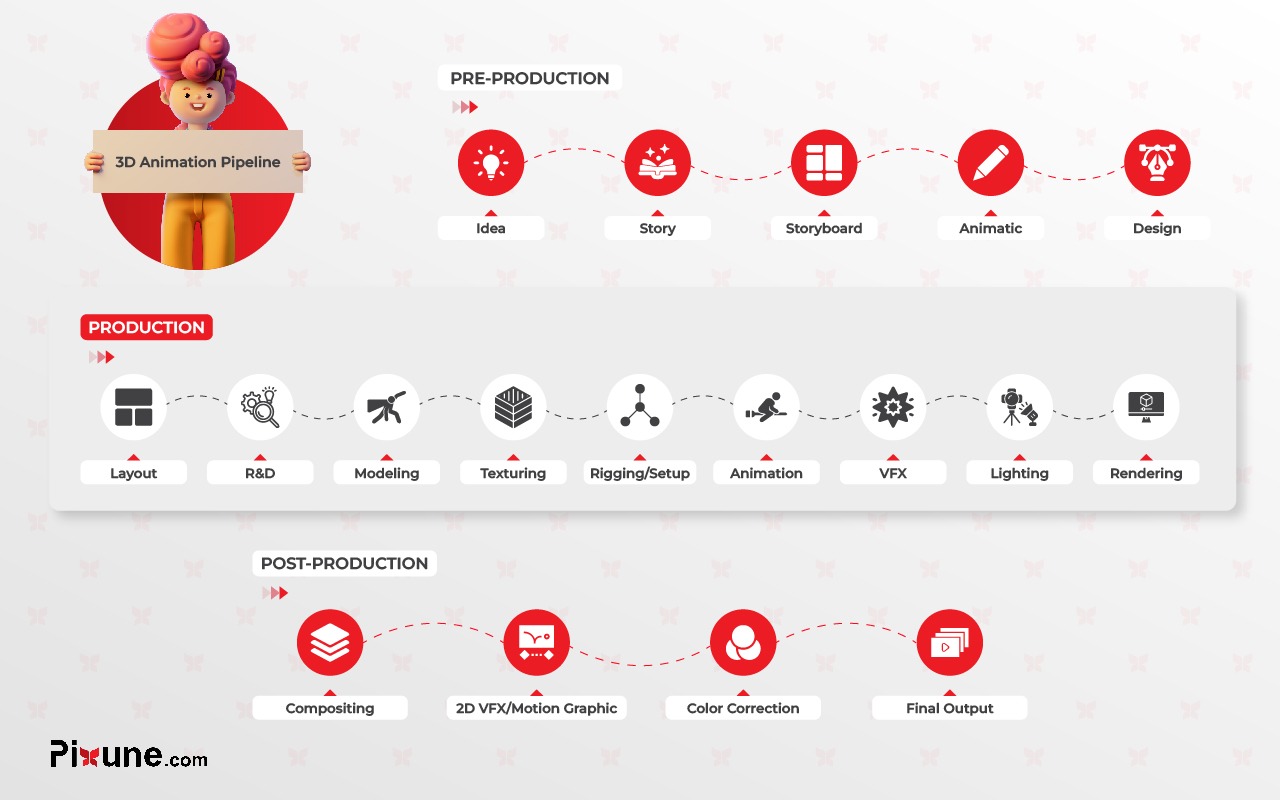
Pre-Production Process in Animation
Two teams in the 3D animation studio are involved in the pre-production; the design team creates the idea, story, and design concepts. And the management team makes the production plan, including budgets, teams, and time frames at the same time.
The pre-production includes the following stages in 3D animation pipeline:
Stage | Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
1 | Define Your Animation Idea | |
2 | Create Your Story | |
3 | Draft Your Story | |
4 | Plan Your Scenes | |
5 | Plan the Movements | |
6 | Define the Visual Approach |
1) Generate an Idea
First, you should know how to start an animation project; the entire project of an animation begins by creating the concept according to the 3D animation pipeline. A brilliant idea can make your story unique, which is why some stories have great content.
When considering animation ideas, remember that ideas need to be innovative but also accessible. Understanding your audience’s taste is an integral part of the process. A good idea forms the rest of the animation around it. On that note, an idea is as good as how you develop it. Even the best ideas can suffer from improper development.

2) Create the Story
Developing the idea is what is going to happen in this step. Story making will provide a clear idea to the artist to choose or design possible locations, characters, story arc, conflict, resolution, etc.
Technology has brought us even more ways to tell our stories.
- You can tell a story by words (written or spoken)
- Images -Storyboard- that tell a story
- You can also combine those two ways and tell a story through words and images
3) Write the Animation Script
The animation script is formal writing in detail about the story. The script must include possible locations, characters, story arc, conflict, resolution, etc.
There are two types of scripts. The first draft of a script is more like a play script, and the writer does not go into technical details when writing it. The first draft is only supposed to tell you a story. The first script is green-lighted for production, and the director or scriptwriter will turn it into a technical script with details.
4) The Storyboarding
Storyboarding is where you create a static and unmoving vision of the script. Cover the script with captions describing the story outline, including the camera staging, character poses, and event scene. Click here to download the free storyboard template.
It plays a vital role throughout the production stage and helps you minimize risky moves in a project. Starting an animation project without a storyboard is like building a structure without a blueprint, so you should know how to make a storyboard. It is the best way to show your visual ideas in 3D animation pipeline.
5) The Animatic
In the 3D animation production process, we can do different types of storyboards with simple models called animatics to show the scene and movement with better details. The simplest animatics are stale pictures drawn and then shown in sequence.
An animatic is defined as a series of images played in sequence, often with a soundtrack. Animatics are used to plan an animation. They are the precursor to the final animation and a vital part of the planning process.
6) Concept Art
The final look of the 3D animation project is decided at this stage. The design adds details and includes the character, costume, concept, prop, and environment design. The style can be as realistic or artistic as you like in the concept art process.
At this point, you need to start drawing character concepts. In concept art services, directors usually ask for several sketches for character designs to be able to choose the one that fits the story best.
Production Pipeline for 3D Animation
There are two teams involved in pre-production; the design team which creates the idea, story and design concepts. And the management team makes the production plan, including budgets, teams, and time frames at the same time.
The pre-production includes the following stages in 3D animation pipeline:
Stage | Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
1 | The 3D Version of the Animatic | |
2 | Build the Geometric Surfaces | |
3 | Apply Realistic Textures | |
4 | Add a Digital Skeleton | |
5 | 3D Animation | Give Motion and Feeling |
6 | Create Complex Elements | |
7 | Set the Mood of the Scene | |
8 | Give a 3D Look |
1) 3D Layout
It is the first step in production, in which the layout artists decide what will be on the screen based on the storyboard. Layout in 3D animation is a 3D version of the animatic using size, shape, environment, and proxy geometry.
2) 3D Modeling
3D modeling is an essential part of making 3D character models – especially humans and creatures – is paying attention to circular muscles (like mouth and eye muscles).
It is the most important step in the 3D animation pipeline. Modeling is when the animation modeler builds the geometric surfaces to give realistic detailing to the characters and objects using 3D modeling techniques. We have also talked about 3D modeling costs and time in our blogs.
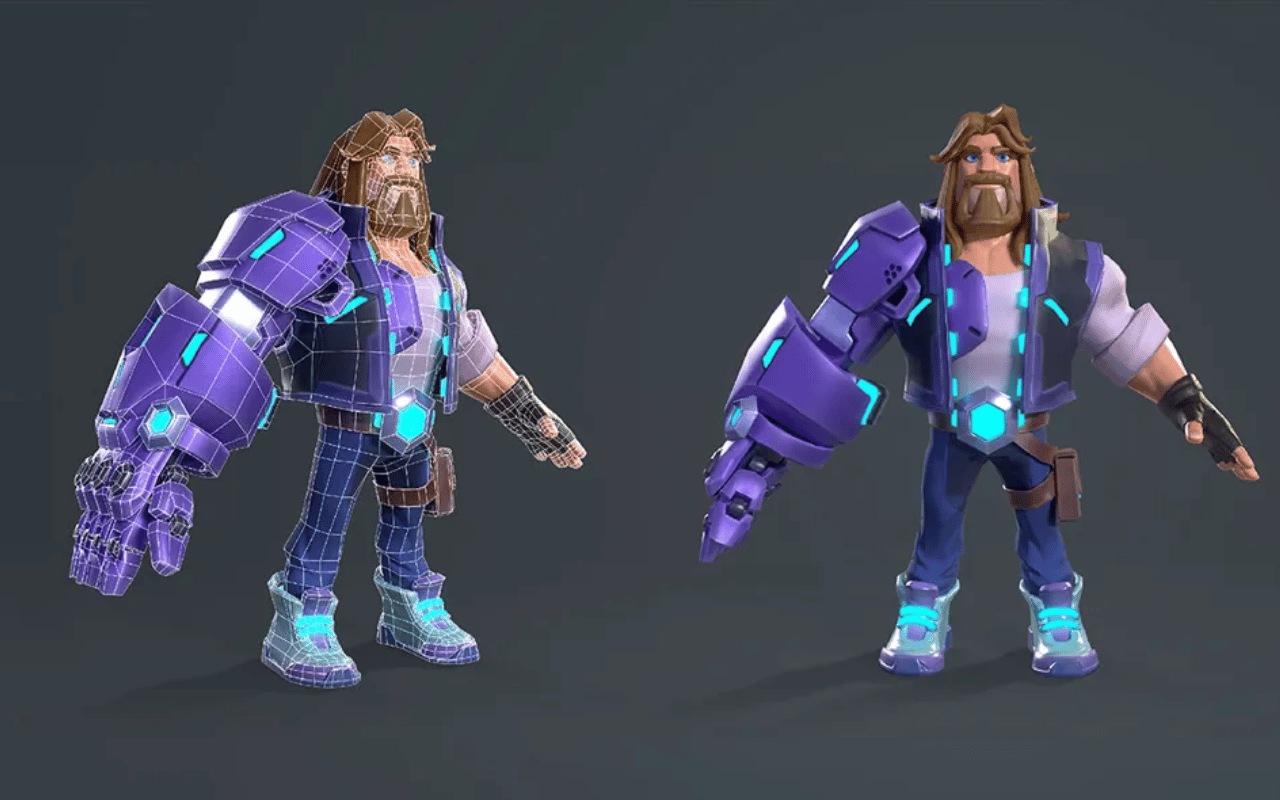

Read More: 3D Modeling vs. 3D Sculpting
3) 3D Texturing
3D Texturing involves taking a 2D image and “wrapping” it around the 3D object. Here the artist applies realistic textures like color, clothing, hair, and surface properties to make characters and locations look smoother and more beautiful.
After finalizing textures on color keys, you can use them in 3D environments and models. The trick in 3D texturing services is implementing something from a 2D picture on a 3D object.

4) 3D Rigging
In 3D rigging services, a skeleton structure is put into the 3D character or object so the animators can move different parts of the geometric object or character as quickly and efficiently as possible. Each character moves differently and has a unique way of rigging.
For example, your characters do not have as many bones as real people or creatures. Humans have 32 backbones, but you do not need that many bones in your characters. It would be best to use as many bones in your model as you need.
5) 3D Animation
It’s time for the most critical but time-consuming stage. This stage is where the movements, position, rotating, and even scaling to mimic different poses are created and give the animation the feel of motion. In some 3D animation uses, characters need accessories like hats, shoes, glasses, and backpacks. Artists should design these objects so that animators can switch between different states of them with relative ease using animation trends.
6) Visual Effects (VFX)
VFX in 3D animation refers to digital effects that enhance animation and film shots or stills. VFX artists often combine live-action techniques with computer-generated graphics (CGI) to create characters, environments, or elements that would be difficult or impossible to capture in real life.
VFX artists combine traditional animation and fine art techniques with cutting-edge technologies, including motion capture, digital fabrication, and computer rendering, to take advantage of 3D animation.

7) Lighting
3D animation requires lighting based on the pre-production phase to support the story, convey the mood of a shot, and visually depict the location, time of day, and even the weather convincingly.
Combining lighting techniques can make the set or the model look realistic.
8) Rendering
What is rendering in the 3d animation process? The final part of the 3D animation pipeline is related to 3D rendering services. In this step, each scene is rendered separately into lots of layers, including background, colors, foreground, highlights, shadow, and objects, to give a 3D look.
Post-Production in 3D Animation
In the 3D animation pipeline, post-production is the last phase where the final touches are added to the project before delivery.
Stage | Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
1 | Put All Layers Together | |
2 | Provide the 2D Details | |
3 | Make the Colors More Realistic | |
4 | Final Output | Choose the Best Format |
1) Composting
Now it’s time to bring all separated layers together in post-production. It can be as simple as putting two layers or as complex as putting hundreds of layers.
2) 2D VFX
Visual effects like sparks, dust, clouds, raindrops, skylining, and camera shake are more easily achievable in 2D than in 3D. 2D VFX provides the 3D quality to all the minor details of the scene and animation.
3) Color Correction
The last step of the 3D animation pipeline is related to colors. You can make the last adjustments to the color, contrast, light, highlight, sharpness, and temperature of the image to create a more realistic look.
Read More: Color Definition in Art
4) Final Output
There are a variety of output formats in the pipeline. The most popular digital format is compatible with most digital devices and can easily be played on the internet.
Why Do We Use a Pipeline for 3D Animation Production?
Generally, there are four main reasons for using a pipeline in 3D animation production:
- Time Management
- Financial Management
- Team Management
- Structure Management
1) Time Management
3D animation production takes a long time, particularly in animated movies and series. A specific production time for each stage in the 3D animation pipeline is required, and a great plan is needed to coordinate many creative tasks, if not even minor micro-delays, in each step, postpone the outcome, and lead the project toward a financial disaster.
2) Financial Management
The cost and budget of every 3D animation depend and vary upon multiple factors. Most project managers and teams estimate the project expenses and the 3D animation cost in the pre-production phase to have a plan for it.
3) Team Management
There are multiple groups of people working on a 3D animation project. The number of people can vary; maybe five people are enough, sometimes hundreds. According to the need, these members are divided into teams.
4) Structure Management
Structuring and standardization in the pipeline is the best way to ensure everyone is working toward the same goal. The top 3D animation companies prefer structuring to keep the balance of all activities on time.
Conclusion
Creating a 3D animation is long, time-consuming, costly, and complex. It requires a list of activities and a professional team with different skills. The final product can be a 3D model, video game, animated film, television show, or marketing video with this animation pipeline procedure.
Fortunately, the 3D animation pipeline is a system that keeps all of the project’s moving parts efficient and up to quality standards. The pipeline differs a bit depending on the project, But the same core principles hold for all of them.











4 Responses
The post covers everything from pre-production to post-production of the 3D animation pipeline. Providing practical advice on how to navigate each step is my favorite part.
Thank you for sharing your thoughts on the post! If you have any further questions or comments, feel free to let me know!
Your article has been a great resource of 3D animation world. Keep up the great work!
Thanks for your feedback! I’m glad to hear that my article has been a helpful resource for you.