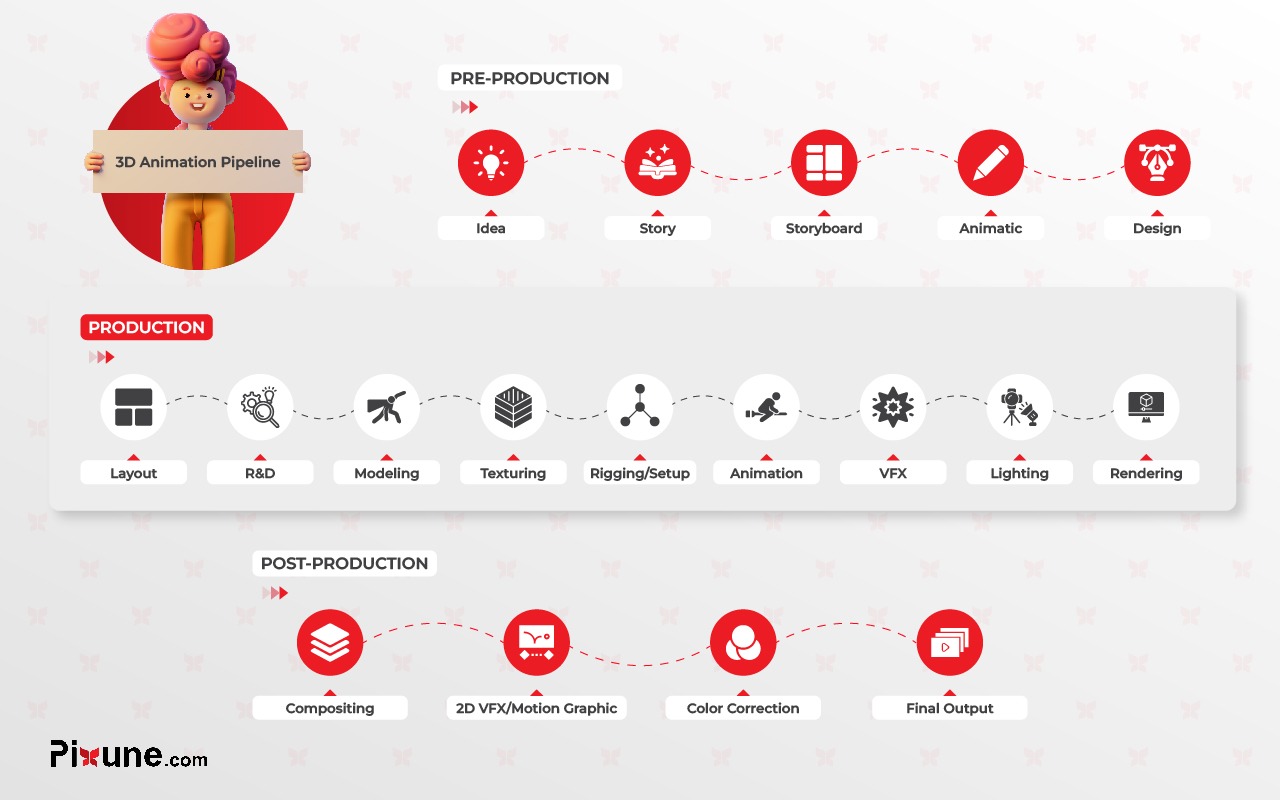
The 3D animation production pipeline is a detailed, multi-phase process that turns ideas into polished animations.
From concept art development to final rendering, every stage is necessary for producing top-notch animation.
Familiarity with the three main phases, pre-production, production, and post-production, prepares artists and every 3D animation studio for a seamless integration of all elements.
In this guide, we will explain each step of the 3D animation production pipeline, provide valuable tips for both professionals and beginners, and explore the purpose of this process to guide you through your journey.

Need 3D Animation Services?
Visit our 3D Animation Service page to see how we can help bring your ideas to life!
What Are the Key Components of the 3D Animation Pipeline?
We can divide the 3D animation pipeline into three key phases: pre-production, production, and post-production.
Each phase encompasses specific tasks such as concept art, modeling, texturing, rigging, animation, visual effects, and rendering.
For a comprehensive exploration of each task, you can follow the links below to understand these concepts in detail.
These three are the key steps for producing smooth and high-quality 3D animations.
What Does the Pre-Production Process in Animation Involve?
Pre-production is the foundational planning phase in animation, where the project’s core elements, like story, visuals, and structure, are developed.
This step involves creating ideas, scripts, storyboards, and designs to ensure a clear vision before production begins.
Let’s discuss the specific components of this phase:
Stage | Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
1 | Define Your Animation Idea | |
2 | Create Your Story | |
3 | Draft Your Story | |
4 | Plan Your Scenes | |
5 | Plan the Movements | |
6 | Define the Visual Approach |
Generating an Idea!
The process begins with brainstorming to create a concept, which can be anything from a theme to characters and worlds.
Then, raw ideas are refined to align with the target audience, tone, and genre.
This step establishes a strong foundation, prevents misunderstanding or confusion, and ensures a smooth workflow during production.
Collaboration among different teams helps shape a compelling and cohesive concept.

Creating the Story!
Once the core idea is set, artists will develop the story by fleshing out characters, defining key plot points, and structuring the narrative.
Writers, art directors, and concept artists collaborate to ensure the story flows logically and fits the animation’s purpose and tone.
This step creates a narrative framework that guides all subsequent stages.
Writing the Animation Script!
The animation script is a detailed blueprint that outlines dialogue, character actions, and scene flow.
It provides a map for timing, pacing, and structure to ensure consistency across the project.
A clear and concise script aligns the production team and serves as a reference for visual and auditory elements.
Role of Storyboarding!
Storyboarding translates the animation script into a visual sequence of sketches, outlining key scenes, camera angles, character movements, and shot timing.
Starting an animation project without a storyboard is like building a structure without a blueprint, so you should know how to make a storyboard.
It helps the team visualize the animation’s flow and make early adjustments, saving time and resources before full production begins.
Click here to download the free storyboard template.
Animatic in Animation!
In the 3D animation production process, we can do different types of storyboards with simple models called animatics to show the scene and movement with better details.
An animatic is an initial version of the storyboard. It incorporates basic animation, timing, and sound.
Animatic tests the pacing and flow of the animation to allow the team to identify and resolve issues early. It ensures the project stays on track before moving to resource-intensive production stages.
Role of Concept Art!
Concept art defines the animation’s visual style, including characters, environments, and props.
It serves as a reference to maintain consistency across the project, ensuring all visual elements align with the original creative vision. Concept artists unify the team’s efforts and set the aesthetic tone. The style can be as realistic or artistic as you like in the concept art process.
At this point, you need to start drawing character concepts. In concept art services, directors usually ask for several sketches for character designs to be able to choose the one that fits the story best.
What is the Production Pipeline for 3D Animation?
The production phase is the core of the 3D animation process, where concepts and plans from pre-production are transformed into assets and animated scenes.
This phase involves creating and animating 3D models, adding textures, rigging, and incorporating visual effects, resulting in the rendering of final frames.
Let’s break down the key steps in the production pipeline:
Stage | Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
1 | The 3D Version of the Animatic | |
2 | Build the Geometric Surfaces | |
3 | Apply Realistic Textures | |
4 | Add a Digital Skeleton | |
5 | 3D Animation | Give Motion and Feeling |
6 | Create Complex Elements | |
7 | Set the Mood of the Scene | |
8 | Give a 3D Look |
3D Layout in Animation
The 3D layout phase sets up scenes by placing basic 3D elements, such as characters and props, within the virtual environment.
Layout artists establish initial camera angles and block out the animation to align with the storyboard.
This step is the first visual step in bringing the narrative to life that ensures the scene’s structure supports the story.
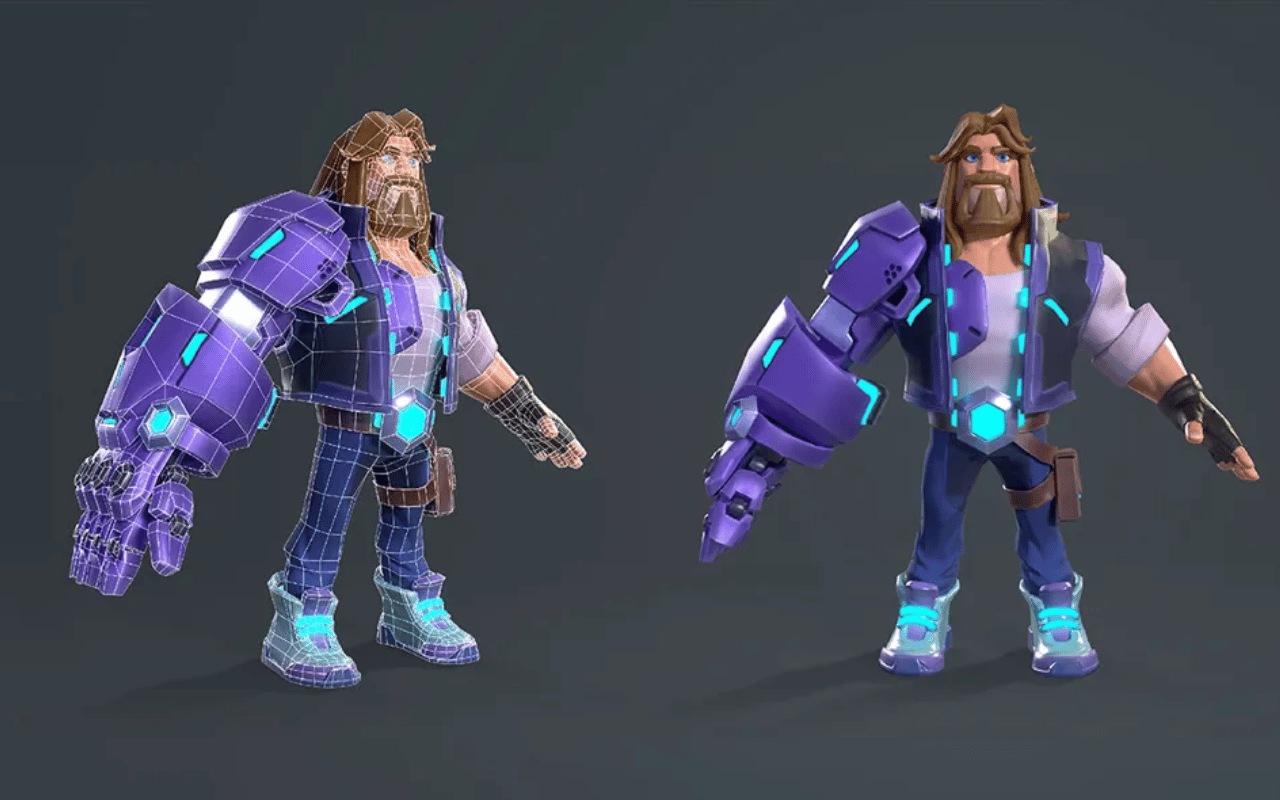
3D Modeling in Animation
3D modeling and 3D sculpting involve creating 3D representations of characters, props, and environments, either from scratch or based on the initial concept art.
These models are built with precision to ensure they are detailed and convincing, since they are the foundation for texturing, rigging, and animation.
High-quality models are made using 3D modeling techniques and are critical for a polished final animation.
You can check out the 3D modeling costs to gain more information about this field.

3D Texturing in Animation
Texturing adds surface details to 3D models using texture maps that define colors, patterns, and material properties (such as wood, metal, or skin).
Textures are a vital component in achieving the desired visual style and emotional impact since they enhance realism and set the scene’s mood.
The trick in 3D texturing services is to implement a 2D image on a 3D object.

3D Rigging in Animation
In 3D rigging services, they create the skeletal framework for 3D models, enabling animators to manipulate their movements.
Rigging artists enable modelers to control how characters bend, stretch, and move, and ensure natural and expressive motion. A well-designed rig is essential for seamless and lifelike animation.
3D Animation
In this step, animators bring models to life by defining keyframes and motion to create dynamic movement.
3D animation involves characters expressing emotions, interacting with their environment, and performing actions, with careful attention to timing, pacing, and performance.
This phase ensures the animation conveys the intended narrative and emotional depth.
In some 3D animation uses, characters need accessories like hats, shoes, glasses, and backpacks.
Artists should design these objects so that animators can switch between different states of them with relative ease using animation trends.
Visual Effects (VFX) in Animation
Visual effects enhance scenes with dynamic elements like explosions, fire, smoke, or weather effects.
Animators create VFX using specialized software to add realism and excitement, thereby elevating the animation’s impact and the audience’s immersion in the story.
VFX artists often combine live-action techniques with computer-generated graphics (CGI) to create characters, environments, or elements that would be difficult or impossible to capture in real life.
Lighting in 3D Animation
Lighting shapes the mood and highlights key elements in a scene. Lighting artists use various light sources, shadows, and reflections to create visually compelling compositions.
Effective lighting transforms flat scenes into immersive, vibrant environments, significantly impacting the animation’s overall feel.
Rendering in 3D Animation
Rendering is the final production step, where all 3D elements, including models, textures, lighting, and effects, are processed into finished frames.
This computationally intensive process calculates every detail to produce high-quality images or sequences to prepare the result for post-production refinements.
What is Post-Production in 3D Animation?
Post-production is the final stage of the 3D animation pipeline, where all elements are refined and polished to create a seamless, high-quality product.
This phase involves editing, adding visual effects, color correction, and preparing the animation for its intended medium.
Below is a detailed breakdown of the key components:
Stage | Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
1 | Put All Layers Together | |
2 | Provide the 2D Details | |
3 | Make the Colors More Realistic | |
4 | Final Output | Choose the Best Format |
Composting in Animation
Compositing integrates various scene elements, such as 3D models, backgrounds, lighting, and effects, into a single, cohesive frame.
This process ensures all layers align perfectly, with final tweaks to enhance the visual composition.
Compositing unifies the animation’s components and provides a polished and professional look.
2D VFX in Animation
2D visual effects (VFX) are added over the 3D rendered animation to enhance scenes with elements like explosions, magical effects, or particle systems.
These 2D effects add flair or help blend animated sequences with live-action footage, enhancing the overall visual output.
Color Correction in Animation
Color correction means adjusting the animation’s character color palette to ensure consistency, enhance mood, and improve visual coherence.
This process corrects lighting issues, balances saturation, and refines tones to create a visually appealing and unified look that aligns with the project’s creative vision.
Read More: Color Theory in Art
The Final Output!
The final output is the completed animation, fully rendered and composited, with all elements integrated.
After ensuring that it’s ready for release, the polished version is formatted and optimized for its intended platform and transmedia storytelling, such as film, television, or web.
Why Do We Use a Pipeline for 3D Animation Production?
A structured pipeline is essential for 3D animation production as it organizes the complex, multi-stage process into manageable steps, ensuring efficiency, collaboration, and consistency.
This pipeline allows specialized teams to work concurrently on different tasks while maintaining a unified vision.
Without a pipeline, projects risk delays, inconsistencies, and disjointed outputs across scenes and assets.
Now, let’s address how specific management aspects enhance the pipeline:
Time Management
A well-defined pipeline facilitates effective time management by estimating production time for each stage, outlining clear deadlines and milestones, from pre-production to post-production.
This structure ensures smooth transitions between tasks like storyboarding, modeling, and rendering, minimizing delays and keeping the project on schedule.
Financial Management
A structured pipeline supports financial management by providing a clear overview of tasks, resources, and timelines.
This allows for accurate budgeting, resource allocation, and cost tracking, ensuring the project stays within financial limits while maintaining high quality, avoiding expensive overruns.
Most project managers and teams estimate the project expenses and the 3D animation cost in the pre-production phase to have a plan for it.
Team Management
Effective team management ensures the pipeline runs smoothly by coordinating departments like storyboarding, modeling, animation, and VFX.
Clear communication and defined roles prevent misunderstandings, reduce redundant efforts, and keep teams aligned, fostering collaboration and maintaining production momentum.
Structure Management
Structure management streamlines the pipeline by establishing transparent processes, responsibilities, and workflows.
It ensures each department knows its tasks and deadlines, preventing bottlenecks and maintaining a steady flow of work.
This organization optimizes collaboration and keeps the production process efficient.
Final Words
The 3D animation production pipeline is a critical framework that guides the path of turning concepts into captivating visuals.
Every phase of this pipeline, pre-production, production, and post-production, is essential for delivering a cohesive, efficient, and visually striking product.
Whether working on a short film, video game, or animated commercial, sticking to the principles of this pipeline ensures a successful outcome from concept to completion!
FAQs
What is the first step in 3d animation?
The very first step is pre‑production, starting with concept development, including idea generation, story, script, and storyboarding.
Why is a pipeline important?
It organizes tasks, ensures clarity, and helps teams efficiently pass work between departments.
Can stages vary by studio?
Yes, while the three phases stay constant, details and workflows differ by studio or project.
How detailed is production planning?
Pre-production lays the groundwork with clear planning to streamline all following stages.
Are VFX part of production or post?
VFX is layered into production, often simulated with physics tools, not reserved for post-production.
How long can each stage take?
Timeline scales with project scope. Pre-production to post can range from weeks to months.
Is this pipeline used across 2D and 3D?
Yes, the three-phase structure applies to both 2D and 3D animation pipelines.







4 Responses
The post covers everything from pre-production to post-production of the 3D animation pipeline. Providing practical advice on how to navigate each step is my favorite part.
Thank you for sharing your thoughts on the post! If you have any further questions or comments, feel free to let me know!
Your article has been a great resource of 3D animation world. Keep up the great work!
Thanks for your feedback! I’m glad to hear that my article has been a helpful resource for you.